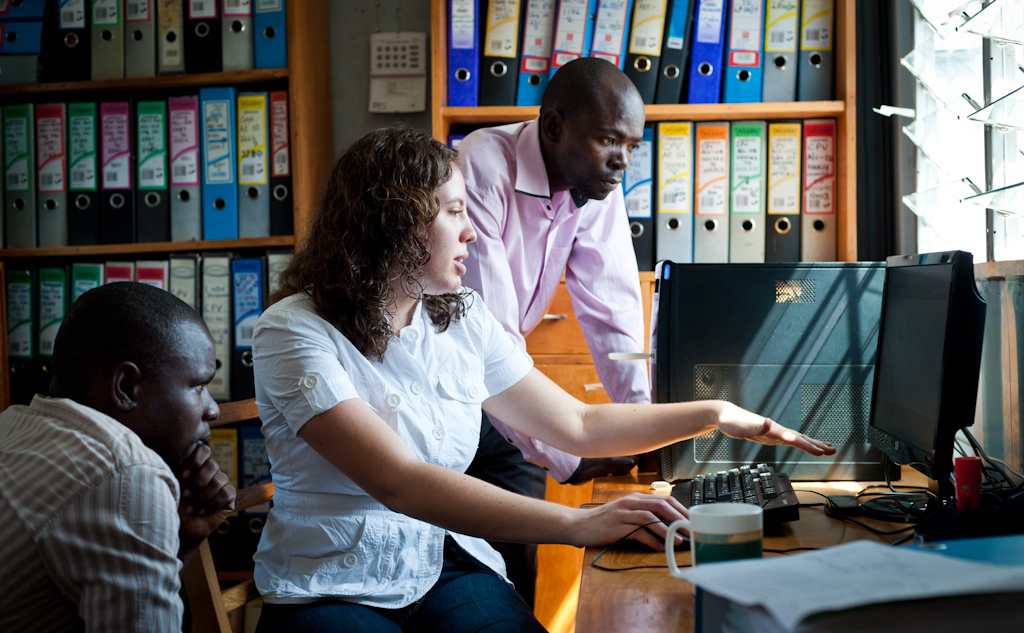
Every few weeks, as we release new improvements and features, we'll let you know on this blog about all of the updates to FrontlineCloud. If you’re curious about our development process, you can read my colleague Sitati’s excellent blog post on the subject, Our Brand of ‘Agile’.
A status update on FrontlineCloud
Introducing FrontlineCloud
The View from 100,000
Here at FrontlineSMS, we’ve been making software for a long time. When we first released Version 2 of our software, a little over a year ago, we were one of a few SMS management platforms available- one of even fewer that was free and open source. At the time, we were proud to have around 25,000 downloads and an active user community. You can imagine our surprise when we checked our download numbers last week and learned that FrontlineSMS has been downloaded more than 100,000 times- more than 75,000 times in a little over a year. We were so excited, we got a cake. You have to understand, when things get serious at FrontlineSMS, we get serious about getting a cake.
FrontlineSMS Survey Results: Can we build accessible software? Yes we can, say our users!
Here at FrontlineSMS, we love data. Like, a lot. If data had its own Facebook page, we’d ‘like’ it and if we took a picture with data out one night, we’d probably make it our profile picture. Data empowers, and we’re all about empowerment o/. In fact, to empower people is the why for the what we do. One thing we’re always wanting to know, of course, is how we are doing. Well we SMSed our friend data to find out – Welcome to the 2013 FrontlineSMS survey results post!
7 Ways Newsrooms Can Boost Citizen Reporting
In my previous post, I argued that established, traditional newsrooms tend to be most comfortable accepting citizen reporting or user-generated content during a large-scale, widespread emergency event. In these circumstances, newsrooms often accept photo and video submissions from the public, or even seek them out on Instagram, Vine or Twitter. Professional journalists or editors may curate tweets or blog posts to summarize the experience of citizens. They may also make a public request for input from those affected, or to clarify incoming information.
Happy 2013: user survey, the release of Version 2.2, and other news!
The development and growth of FrontlineSMS has been driven by feedback we receive from our active user community. Each year we give our users the opportunity to share their use and vision of FrontlineSMS through our annual user survey. This year is no different! We would like to hear from you through our 2013 User Survey - tell us how you're using the software, how we can make it better, and help us show how FrontlineSMS is making a difference. The survey takes less then 10 minutes!
Cooking up a menu of services: Responding to user needs for mobile engagement support
The FrontlineSMS team is pleased to announce a new level of premium support and consultancy services to help users design mobile engagement strategies, build capacity for professional adoption and automate communication workflows. Engaging people on new platforms can be a complex process and it can be a challenge to find a recipe for success. New technologies mean new communication patterns which are inherently personal and constantly changing.
FrontlineSMS at 7: Al Jazeera gives a voice to the people of Uganda via SMS
In the third of our seven blog posts celebrating the month that FrontlineSMS turns 7, Trevor Knoblich, our Media Project Manager reflects on how Al Jazeera, the media house, gave the people of Uganda a voice, via SMS, in response to the controversial Kony 2012 video which went viral a few months ago.
"As the media project manager at FrontlineSMS, I've heard many inspiring stories of journalists and media organizations deploying the software in creative ways. One of my favorites is relatively recent: the FrontlineSMS component of Al Jazeera's Uganda Speaks program. Members of Al Jazeera's New Media team felt Ugandan voices were lacking from the global debate around the controversial Kony 2012 viral video. To help connect Ugandan voices to the debate, Al Jazeera established an awareness-raising campaign, which consisted of showing the video and then inviting Ugandans to post their reactions to the debate via Twitter, e-mail and SMS. They even connected the responses to a map, allowing people from around the world to see where respondents were located.
"I had the pleasure of meeting one of Al Jazeera's New Media team, Soud Hyder, pictured here, and asked him about the project. Specifically, I was curious about the value of SMS in such a campaign. He told me that SMS allowed Al Jazeera to reach people who had no other option for participating in the debate - a voiceless population. 'Text is an equalizer that allows us to elevate more voices, which amplifies the conversation,' Hyder said.
"I've heard similar reactions about our software globally. Many people worldwide have an increasing ability to share and participate in news, but millions more are left out of this conversation. FrontlineSMS, combined with the proliferation of mobile phones around the globe, opens new possibilities for citizen engagement."
We’re collecting photos of our users telling the world how they use FrontlineSMS. If you want to get in on the act, take a photo of yourself or your team holding a piece of paper or a whiteboard telling the world what you do with FrontlineSMS. For example: ‘I monitor elections’, ‘I safeguard children’ or ‘I make art’. You can see a slideshow of the photos we’ve had so far on our Flickr page.
It doesn’t matter what language it’s in as long as it’s legible and if possible you should be able to see from the photo where it was taken, so, if you can, get out of the office!
You can: - post to Twitter or Instagram with the hashtag #FrontlineSMSat7 - email the picture and we’ll post them - post the picture on our Ning network and we’ll post them - post them on Flickr or any other web service and let us know where they are
Welcoming our new Boards of Directors!
We are very pleased to announce that last month we appointed new Boards of Directors, marking the next step in the growth of the FrontlineSMS project and its parent organizations.

FrontlineSMS is a joint project of the US-based kiwanja Foundation and the kiwanja UK Community Interest Company. This trailblazing hybrid structure means that we can continue to push forward and protect the social mission which inspires us - to lower barriers to social change through mobile technologies - in two different ways.
The Foundation continues to provide free, open-source software and freely available support to use it through our website, with over 30,000 downloads to date, an online community of over 2,500 people, and examples of use in over 80 countries worldwide. The Community Interest Company (or CIC for short) works to provide support and services to clients with specific and time-bound needs, designing project, providing training and custom modifications to the platform. Next year will see exciting developments in the way we make the platform available, masterminded by the CIC team.
Overseeing these two organizations are two separate Boards, with our Founder Ken Banks as Chair, Sean Martin McDonald as CEO of the CIC and myself as CEO of the Foundation present on both. Ensuring independent scrutiny and contributing their insight and experience are eight independent Board members, four on each Board.
For the Foundation Board, we're honored to welcome Brenda Burrell, co-Founder of the Kubatana Trust of Zimbabwe and leader of the team providing Freedom Fone, open-source IVR technology for social change organizations; Jan Chipchase, who brings an anthropologist's eye and approach to technology design as Executive Creative Director of Global Insights at Frog Design; Linda Raftree, a leading voice in ICT for development and an experienced implementer of FrontlineSMS while working with country teams at Plan International; and Jeff Wishnie, architect and proponent of many open-source tech collaborations throughout his career and most recently as Director of Social Impact at software development consultancy ThoughtWorks Inc.
 We've also added four members to the CIC Board: Trip Allport, III, the International Program Director for Africa for Accenture Development Partnerships who brings his considerable experience in building consulting practices in low-resource environments; Diane Coyle, a best-selling author, economist, and leader who focuses on the impact of technology on emerging markets; David Edelstein, who has years of experience designing and supporting business models around mobile technologies as the Senior Vice President of Solutions and Regions for the Grameen Foundation; and Joel Selanikio, the Co-Founder of DataDyne, whose tool, EpiSurveyor, is a leader in mobile data collection (Joel is also a practicing physician at Georgetown University Hospital).
We've also added four members to the CIC Board: Trip Allport, III, the International Program Director for Africa for Accenture Development Partnerships who brings his considerable experience in building consulting practices in low-resource environments; Diane Coyle, a best-selling author, economist, and leader who focuses on the impact of technology on emerging markets; David Edelstein, who has years of experience designing and supporting business models around mobile technologies as the Senior Vice President of Solutions and Regions for the Grameen Foundation; and Joel Selanikio, the Co-Founder of DataDyne, whose tool, EpiSurveyor, is a leader in mobile data collection (Joel is also a practicing physician at Georgetown University Hospital).
We can't wait to work with such a passionate, engaged group to make our organizations the best that they can be, and are wholeheartedly grateful for their support and commitment.
Data-mining our download records - what download registration did, and didn't tell us about our users
By Kavita Rajah and Laura Walker Hudson FrontlineSMS software is used in such a wide variety of sectors that often people are surprised to hear that the inspiration for FrontlineSMS originally came specifically from conservation work. Throughout 2003 and 2004, FrontlineSMS Founder Ken Banks was working to find ways to help authorities engage and communicate with communities in wildlife conservation in South Africa, without relying on the Internet. Ken realised he needed a system that could send, receive, and organize text messages through a mobile device and a laptop without needing the Internet, and from that the original concept of FrontlineSMS was born. The software was developed in the summer of 2005 and made available online that October.
Six years on, despite the very context-specific inspiration for the software, FrontlineSMS has now been downloaded nearly 27,000 times and is in use in over 80 countries, in 22 different areas of social change work. Until the recent release of FrontlineSMS Version 2, users were asked to fill in a form telling us who they were and how they were planning to use FrontlineSMS before being given a download link. Following up on this data gives us the links with users that lead to our case studies and FrontlineSMS in Action blog posts. We recently analyzed the whole dataset to learn more about how, why and where people seek to use our software. What we were able to glean from it was interesting. Among other fun facts:
- The top 3 sectors in which FrontlineSMS is being used most are Education, Health and Civil Society
- The country that has downloaded FrontlineSMS the most is the United States, followed by Kenya and then, India - we think that a lot of downloads from North America and Europe are intended for use elsewhere
- Africa accounts for 35% of all downloads - more than any other continent. 25% of downloads are from Asia, and 17% from North America.
Interestingly, some geographic regions have large numbers of downloads in certain sectors. For example, West Africa has the highest number of downloads in Election Monitoring and Engineering, while Europe has the highest number in Arts and Culture. Asia has the highest number of downloads in the Media sector.
However, the limitations of this dataset got us thinking about how we gather information on our users.
Gathering data about how FrontlineSMS is used is critical for us on a number of fronts - it helps us to improve the software, enables us to report to our donors and the public about the impact of our work, and helps inspire others to use SMS in their work in new and more powerful ways. Although the download data was useful, it could only give us a snapshot of a user's intention at the time they downloaded FrontlineSMS - it was difficult to link this with data about actual use, from the statistics-gathering module in version 1.6 or later, or from our annual user survey, and many users didn't go on to use FrontlineSMS as they'd intended. The most informative element of the form was a freetext section which allowed users to give us potentially quite a bit of information about our plans - but is hard to parse and analyze and often included hardly any data. The only way for users to download anonymously was to give false or junk information on the form.
When we came to plan the release of the new software, we thought very differently. Version 2 of the software is a one-click download that asks users to register when they install. Information collected in this way is sent back to us over the web, when the system sees the internet - we'll be adding support for registration via SMS later. We are committed to allowing users to maintain their anonymity, as we know many are activists (if you are one of these people, you should read our Data Integrity Guide!). You will always be able to opt-out of in-app registration - although it means we get fewer registration records, we know we can trust the data we get. In future, we'll also be building better ways for users to keep in touch with us and each other, and share information about what they're doing with FrontlineSMS, using the website.
We'll keep analyzing the data and posting updates here - in the meantime you can read the analysis of our 2010 and 2011 user surveys here.
Speak a language and want to support FrontlineSMS? We need version 2 translated into French, Spanish, Mandarin, Russian and Arabic and every other language you can think of...
We launched FrontlineSMS Version 2 in English and Swahili – now we need to ensure that users all over the world can use the software.
We need to translate the terms and messages used in Version 2 into five priority languages: French, Spanish, Mandarin, Russian and Arabic – but we’re looking for speakers of all languages to contribute translations in their native tongue. Translators will join our team of FrontlineSMS:Heroes – volunteer coders, testers, analysts and designers who contribute their time to the project for free, and as a thank you are featured on our website and get to sport these very fetching tshirts.
FrontlineSMS V2.0: A Powerful Tool for Achieving Positive Social Change and Health Improvement in Developing Countries
Good news from the software sector: FrontlineSMS Version 2 is here at last! Two years in the making, the updated version is simpler, more intuitive, and easier to utilize. It also adapts more easily to individual needs and systems, and has already met an enthusiastic response from the SMS community. And with all it has to offer, the new software should prove a valuable contribution in the effort to achieve positive social change in developing countries around the world.
FrontlineSMS is a free, open source, SMS-messaging software that empowers the user to communicate with large groups of people through a mobile network. Basically, with just a laptop and a mobile phone, the initiator can create a communications hub that allows him to send, receive, and manage text messages.
The software is easy to set up and doesn't require an Internet connection—an important feature, since many FrontlineSMS users come from remote areas where reliable Internet connections simply don't exist. (The software has a significance presence in underdeveloped parts of Africa, for example.) Uniquely equipped to serve remote areas and the local communities who live there, FrontlineSMS is a powerful tool for achieving positive social change and health improvement by breaking down communication barriers and allowing instantaneous, two-way exchanges of information.
FrontlineSMS: Version 2
As an organization, FrontlineSMS offers individualized training and support to organizations embarking upon social change projects. It is also very proactive about acquiring user feedback and incorporating it into software updates and new releases. From the start, FrontlineSMS has focused on meeting the actual needs of local people by consistently engaging its user base.
FrontlineSMS Version 2 incorporates an extensive amount of that user feedback and represents “a significant step forward.” As an overall assessment, the software is said to be “easier and more intuitive to use, more versatile, and capable of being more easily extended with new functionality.” (For a detailed overview of the changes and additions, consider this description from the FrontlineSMS web site.)
A stronger and more flexible architecture allows the software to be integrated into more platforms and systems, and permits users and developers “to customize FrontlineSMS to better meet their needs”. So far, the response to FrontlineSMS Version 2 has been enthusiastic.
In addition to its core software, FrontlineSMS offers four sector-specific programs:
- FrontlineSMS:Credit (“enables organizations to easily manage mobile money”)
- FrontlineSMS:Legal (“increases the reach, transparency and efficiency of legal systems in underserved areas”)
- FrontlineSMS:Learn (“supports and strengthens] education and training initiative and human capacity development”)
- FrontlineSMS:Radio (“represents a vital outreach particularly for rural communities” and “[fosters] two-way dialogue”).
FrontlineSMS:Learn and FrontlineSMS:Credit are currently running on Version 1.7, but will eventually be updated to the full-scale Version 2.
FrontlineSMS: Valuable Social Change and Healthcare Tool
Today, FrontlineSMS is used in over 80 countries. Not surprisingly, its usage remains concentrated in developing countries where mobile technology continues to increase dramatically. According to this report, the number of globally-sent texts tripled between 2007-2010. The numbers add up to 6.1 trillion texts, all told, or 200,000 texts sent each second. Mobile technology is a powerful communication tool in the developing world, and FrontlineSMS has had no trouble tapping into it.
“If you go to the developing world and you look at how cellphones are being used you can really see that people are already doing this kind of organizational management, communicating with stakeholders, communicating with people they're working with and for,” Laura Hudson, FrontlineSMS CEO, stated.
A recently-released survey confirms the organization's growth and success. Currently most users are located in Africa, but there is a growing presence in Asia, India, the Philippines, Malawi, and Pakistan. Around 78% of FrontlineSMS users belong to grassroots non-governmental organizations (NGOs) operating in developing countries. As an open source product, FrontlineSMS is highly adaptable and thus valuable in situations and projects requiring low costs and ample flexibility. The fact that no Internet and only basic tools are required (laptop and mobile phone for the initiator; mobile phone for the receiver) is also an immense help. This arrangement allows the software to be used on the road or during power outages, for instance. Thanks to FrontlineSMS, NGOs have been better equipped to address human rights issues, manage natural resources, provide disaster relief as well medical care and supplies to remote regions, organize political protests, collect field data, conduct public surveys, educate the public on various topics, and much more.
Take Burundi as an example. In an African country where political elections often provoke violence and catch ordinary citizens in the crossfire, FrontlineSMS has proved useful. During election season, the Great Lakes Region of Africa (AGLI) teamed up with the Healing and Rebuilding Our Communities (HROC) program and created the Burundi Election Violence Prevention Program. The 750 participants used FrontlineSMS on their mobile phones to monitor election sites by reporting arrests or violent incidents, sending out alerts if irregularities or unsafe situations arose, and keeping each other up to date on the situation. In one instance, participants communicated with the police via FrontlineSMS to secure the release of an innocent citizen who had been arrested.
Likewise, in Indonesia, rural farmers in West Kalimantan have used FrontlineSMS to “report, connect, and raise awareness of their issues” in an area dominated by a contentious palm oil industry whose activities have sometimes caused problems for the farmers. By partnering with the local news station, Ruai TV, farmers have raised awareness of the situation and made their voices heard; by using FrontlineSMS, farmers are able to keep each other up to date on situations, back each other up during conflict, and mobilize as a unified group.
Or consider an offshoot organization like FrontlineSMS:Credit. In Africa, where economic development is severely hampered by lack of rural banks and stable monetary systems, mobile payment through SMS services is a huge development that eliminates problems caused by delivering cash payments over long distances. Without mobile money, for example, farmers wait “weeks or months” before receiving payment, and the employees who deliver those cash payments must travel long distances--sometimes through unsafe areas. FrontlineSMS:Credit saves time and reduces the risk of traveling with large amounts of cash, increasing efficiency and allowing workers in all sectors to focus on farming, delivering quality healthcare, or whatever their jobs entail.
The system also works as a kind of rudimentary SMS Craigslist. Users of the full suite and post notices of the products and services they offer or are seeking. This has been a boon, for example, for farmers who have significantly expanded their market and thus can obtain better prices while buyers are able to purchase high quality food at fairer prices. By supporting free market local economic activity, FrontlineSMS makes highly nutritional food more available and helps alleviate food shortages.
It may be relevant to our readers that FrontlineSMS, in addition to being used as an agent for social change, maintains a powerful presence in the healthcare sector as well. Almost right from the start, it was used to improve care coordination at a poverty-stricken health clinic in Malawi. Since then, its application to healthcare has only expanded. Consider these examples:
- In Cambodia, Sophie Baron is working on a pilot study to monitor and contain animal diseases that present a significant threat to agricultural livelihoods. In conjunction with the CIRAD, IPC and VaVRI, Baron is testing a system designed to monitor animals' deaths and diseases in local farming areas. Weekly reports allow workers to track diseases, discover the source of an outbreak, and keep tabs on the general situation. According to Baron, “Receiving regular data via SMS—and being able to manage this data within FrontlineSMS—helps enable NaVRI to adopt more timely and effective response mechanisms to breakouts of animal diseases.”
- Cleopa Otieno, National Coordinator of KenTel, uses FrontlineSMS to text people living with HIVin Kenya. The program is (or was, as of November 2011) still in the works, but a pilot study enabled telehealth centers to provide victims of HIV with information concerning health and prevention of infection and disease. As it grows, the program will become more and more interactive, encouraging participants to make the most out of the resources available.
- In Kenya and Uganda, Stop Stockouts is lobbying for the African governments “to meet their obligations to provide essential medicines” by increasing the national budgetary allocation” for purchasing medicines and “by ensuring efficiency and transparency in the procurement, supply, and distributions of medicines.” Stock-outs (which occur when a health center or pharmacy runs out of a medicine) can significantly delay treatment and subject patients to serious and aggravated health risks. Stop Stockouts relies on FrontlineSMS for campaign communication and monitoring of medicine availability.
- In 2011, the Institute for Reproductive Health partnered with FrontlineSMS to provide an mHealth service called CycleTel, which “helps women take charge of their reproductive health and use an effective family planning method” by empowering them with knowledge about their days of fertility and so forth. IRH used FrontlineSMS to manually test the CycleTel program in two Indian cities, Lucknow and New Delhi. The software proved to be “a crucial and practical step in the technology development process” and contributed to the overall product.
FrontlineSMS: The Ongoing Story
The idea for FrontlineSMS began with a conservation trip to South Africa in 2004. Ken Banks, working with authorities to establish better communication with nearby communities, realized the need for tools that would enable information exchange in remote areas. In places like Africa, NGOs typically lack money, expensive equipment, and reliable access to Internet and electricity—but they do carry mobile phones. At the time, there was no group-SMS system in existence that could operate in remote locations, so Banks decided to make his own: “I wrote the software in five weeks at a kitchen table,” he says in this article for National Geographic. “I made it a generic communications platform that could be used for almost anything, and I made it free.”
Although he wrote the software to fix a specific problem, Banks also focused on creating software that was adaptable to different situations and purposes: “I also felt that other disciplines – health, agriculture, education and human rights among them – were no different, so FrontlineSMS did not seek to solve a particular problem in a particular place, but sought to be an all-purpose tool, and be all things to all people.”
FrontlineSMS has successfully scaled communication barriers and provided catalysts for social change and healthcare improvement in more than 80 countries worldwide. (Not bad for an organization that hired its first employee in 2009.) Made available online in 2005, FrontlineSMS was transferred to an open source platform in 2008. The same year, Banks started working with Josh Nesbit (co-founder of Medic Mobile) on a project to improve management and patient care at a clinic in Malawi. The project stirred up a wave of eager interest and encouraged other people and NGOs to adopt FrontlineSMS for their own projects and organizations.
Since then, the software has continued to garner praise and recognition. The year after Ken Banks worked with Nesbit at the Malawi clinic, FrontlineSMS won the Silicon Valley Tech Award and received funding from OSI, the Hewlett Foundation, and the Rockefeller Foundation. In 2010-2011, founder Ken Banks was named an Ashoka Fellow as well as a National Geographic Emerging Explorer, and carried off the Pizzigati Prize to boot. Meanwhile, FrontlineSMS won the Curry Stone Design Award in 2011. The software has been downloaded over 25,000 times, and has had a profound impact upon the lives and livelihoods of many communities in developing countries, especially Africa.
Meanwhile, FrontlineSMS is passing by another milestone in its history. This May, founder Ken Banks announced his intention to step back and take a more relaxed role in the organization, choosing to focus on other projects which a full-time commitment to FrontlineSMS had prevented him from developing (details will be posted on his blog). Laura Walker Hudson and Sean Martin McDonald, future CEO of kiwanja Foundation and CEO of kiwanja Community Interest Company, respectively, will lead FrontlineSMS forward to the next stage of its development.
Regarding that next stage, Banks is optimistic: “It’s an incredible time to be working in the field of technology-for-social-change, and I’m excited about the future for FrontlineSMS, its users and the team behind it,” he reflects in his transition announcement on the FrontlineSMS website.
If the past is any indication of the future, there's good reason to feel excited. In just a few years, FrontlineSMS has built a strong history of continued growth, successful problem-solving, cultural outreach and technological advancement. Innovative, low-cost, and flexible, FrontlineSMS is uniquely poised to make a difference in the developing world. And the good news is, it already has. So here's to the new and improved FrontlineSMS.
Context is King: Knowledge Sharing on Communications Tools at BBC Media Action
 By Amy O’Donnell, FrontlineSMS:Radio Manager
By Amy O’Donnell, FrontlineSMS:Radio Manager
Recently my colleague Flo and I visited BBC Media Action for a Knowledge Sharing session which focused on the use of innovative mobile technology to enable effective communication for social change. BBC Media Action (previously known as the World Service Trust) "uses media and communication to provide access to information and create platforms to enable some of the poorest people in the world to take part in community life. With a focus on programming that directly engages people in debate and discussion thereby encouraging communication across political, ethnic, religious and other divides in society." We felt lucky to be one of the last visitors to their longstanding home in the iconic Bush House, London as the BBC is relocating from there after 70 years.
Often when people first hear about FrontlineSMS, it’s not just the software which inspires them, but the valuable lessons we learn from how the tool is being used. BBC Media Action works to directly engage people in debate and discussion through programming and this workshop explored the potential of SMS to open up participation.
To broaden participation, combine accessible communications channels
We explored how a radio station in Uganda is using FrontlineSMS to gather incoming audience feedback via SMS to put their questions to MPs while on-air; how FrontlineSMS is engaging citizen journalists in Indonesia and how the software is being used to run a news service for women in Sri Lanka. Introducing another popular open-source platform, we explained how the Ushahidi mapping tool was used in conjunction with FrontlineSMS for election monitoring by the Reclaim Naija project in Nigeria last year to illustrate reports in relation to their location. Many of these programs use SMS in concert with other platforms, whether radio, TV or the Internet - an important element of building a truly accessible, system that works for its unique context.

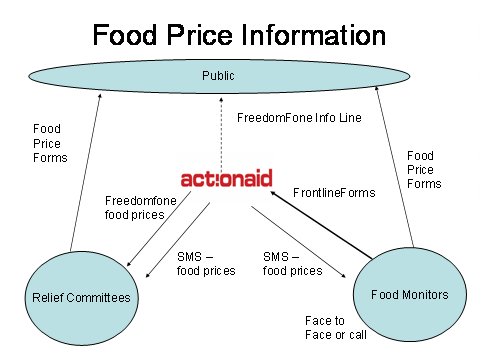
BBC Media Action’s own Jonathan Robertshaw shared his experience of using FrontlineSMS as a practitioner. He explained BBC Media Action’s role in a project run by ActionAid and infoasaid which which set up a food distribution alert and food price information system in Kenya in the aftermath of the 2011 drought. The project successfully took a multi-platform approach to improving communication between relief committees, food monitors and the public. The set-up gave people options, including voice (using an interactive voice-based software called FreedomFone); detailed SMS-based data collection (using FrontlineForms, FrontlineSMS’ data collection tool); and text message (using FrontlineSMS’s core platform).
Technology is 10% of the solution
As the discussion with different Media Action project leaders delved into program specifics, we explored how technology often only represents a small proportion of overall project design. Looking at potential Media Action projects - including participatory audio dramas and humanitarian radio - reinforced how important it is not to lose sight of behavioral and cultural factors as well as critical delivery planning: outreach, messaging, integration, translation, verification and impact monitoring. One of the group asked how to anticipate the resources required to run a communication platform. Particularly when the volume of response depends on the level of interactive behavior, the group agreed there is no “one-size-fits-all” or “magic formula.” Program staff have to consider the context and stay flexible, tweaking the system to respond to the needs of their beneficiaries and staff as they develop. Resourcing this kind of responsiveness is critical and difficult, and there are costs in money and goodwill involved in introducing people to a new system, changing messages and systems too often. The group agreed that, rather than committing to services which it may be difficult to estimate demand for, organizations should manage expectations and try to test ahead of time. Trying out communications in small trials or pilots can help scope people’s reactions.
The strongest message we took away from the session was practitioners’ motivation to learn about the different tools available in the communications toolkit. Often the design of a communication system is not about one tool, but the right tool or right combination of tools which suit the context. FrontlineSMS needs limited support and people are implementing projects all over the world using the software and tools readily available to them without requiring our team’s direct involvement. We're proud of how much that makes it a really sustainable piece of software for organizations working in the last mile, and a critical tool for long-term capacity-building.
Why Version 2? The story behind the FrontlineSMS redesign
 Three weeks ago, FrontlineSMS launched its first new full release in over a year. Today, we're releasing version 2.0.2, which includes useful bug fixes and small tweaks to the functionality that make it even easier to use. You can expect regular releases from us from now on, with new features coming out every couple of months. Check out our launch blog post, and our Version 2 microsite, for more information about the software. In this post, we wanted to share more of the background to the decision to rewrite our software from the ground up, and some of the key principles that have informed our work over the last eighteen months.
Three weeks ago, FrontlineSMS launched its first new full release in over a year. Today, we're releasing version 2.0.2, which includes useful bug fixes and small tweaks to the functionality that make it even easier to use. You can expect regular releases from us from now on, with new features coming out every couple of months. Check out our launch blog post, and our Version 2 microsite, for more information about the software. In this post, we wanted to share more of the background to the decision to rewrite our software from the ground up, and some of the key principles that have informed our work over the last eighteen months.
Extendability
In late 2010, we were working with Medic Mobile, Dale Zak, Ushahidi and others to build extensions to FrontlineSMS which would allow users to manage more complex contact records, map reports offline, and build in scheduled SMS to the platform. Version 1 of the software was tough for volunteer coders, or other partners, to extend. Without APIs, any alteration had to be hard-coded into the software, and plugins were hard to make inter-operable with one another.
The crunch point came when we asked Alex, our Lead Developer, how long it would take to build the kind of Contact Records Management (CRM) we wanted into the platform - he told me it would probably be quicker to start again. We realized that every time we wanted to respond to user needs and add a new feature it would be an additional delay and drain on our resources. Building extension code into the core software was always going to be a mammoth task. So we started looking in earnest at the possibility of redesigning the software for a new set of requirements.
Usability
At around the same time, we met Gabe White of Small Surfaces, a user interface design consulting firm in Kampala. With his help, we spent the first part of 2011 interviewing a wide range of existing FrontlineSMS users, and analyzing user survey responses and forum conversations to understand how FrontlineSMS could be improved. Key feedback was that users were used to a certain type of interface in communications platforms, thanks to widely-used services and applications like Gmail and Microsoft Outlook - they wanted to see an inbox, and be able to monitor their sent and pending messages in one place. If FrontlineSMS behaved like other communications platforms they were already familiar with, new users would pick up the basics of the platform more easily.
We had noticed from our 2010 user survey that only a relatively small group of ‘super-users‘ - very tech-savvy, for the most part, and often part of the ICT4D sphere - were using the more advanced elements of FrontlineSMS to reply automatically to messages, allow end users to join and leave groups using SMS commands, and transfer message content to web- or network-based services and databases. We wanted to make it easier for all of our users to branch out and use SMS in more powerful and professional ways. So the design of FrontlineSMS Version 2 is a commitment to helping users to discover more about the platform and use increasingly sophisticated functions. Activities are a simpler way of conceptualizing the keyword functionality that has always existed in FrontlineSMS. Keyword settings, and many other elements of the software, can now be set up using simple walk-throughs, prompting users to make the most of functionality available to them.
Many users commented that, over time, they were accumulating huge numbers of SMS and contacts, but were unable to perform simple operations (grouping, moving and deleting, for example) on multiple SMS or contacts at once. Similarly, without a sophisticated search function, users struggled to maintain control of the backlog of SMS, and find important communications quickly. Manipulating the data in another program required you to download the whole database each time. We have implemented fixes for all of these problems in Version 2. You can now manage multiple SMS and contacts at once, using check-boxes; control search outputs using date-ranges, group membership and other characteristics; and export the SMS received through specific activities at the click of a mouse.
A new developer team
Building all of this has been about a year’s work, all but the very first few weeks of which has been done in Nairobi, Kenya. Alex moved to Nairobi in the spring of 2011 to set up a larger development team, and over the last year we have welcomed David, Geoffrey, Joy, Roy, Sitati, and Vaneyck, with Hussain in London rounding out the team. All of them have contributed hugely to the process of designing, building, and launching version 2 and although some have, or may in future, move on to other things, they will always be part of the team that made this all happen. As we look beyond the launch and begin to plan additional features, we have a fantastic base to build on, from our very colorful offices in the centre of a growing Tech City in Kenya’s capital.
What’s next?
We know we have a lot more to do. Some of version 1’s features, including the Frontline Forms interface and our Translation Manager, are still in the works. Some will come swiftly, such as Subscriptions Manager (which takes the place of the join/leave group keywords in version 1) and which is almost ready. Others are concepts we want to take some more time to get right; such as how Version 2 handles building Forms, and how it will display data collected on a mobile device and submitted through a variety of channels. You can read more about our planned features on our Upcoming Features page.
The whole FrontlineSMS team, including volunteers and fantastic partners like Gabe and the Software Testing Club, have put a tremendous amount of energy into Version 2; we are really proud of it and at the same time we feel like we’re just getting started! We couldn’t have got to this point without our users, who gave us the original inspiration, helped shape the design, and continue to contribute feature requests, testing and the drive to keep improving on FrontlineSMS.
We can’t wait to hear what you do with it.