Nkhotakota Community Radio Station, along Lake Malawi, is a Malawi Communication Regulatory Authority (MACRA) recognized broadcaster and has been in operation for eleven years. More than 500,000 people live within our coverage area- transmissions reach Nkhotakota and Ntchisi districts and parts of Nkhatabay, Salima, Dowa, Mzimbaand Kasungu.
Building Sustainability: Lessons from Swazi Cotton
It’s a simple idea: provide smallholder farmers with information via SMS to improve farming practices and thus increase their yields. In fact it’s a concept that has been replicated by NGOs and MNOs across the developing world, with varying degrees of success. However, the real challenge in launching such a service lies in building a business model that is both commercially viable to the provider whilst remaining accessible to the poorest populations.
Rapid Prototyping and Tech Stewards: reflections on recent field work
At the heart of our project is the community of practice concept, which refers to a group of like minded people connected through a process of social learning. A CoP does not necessarily conform to organizational boundaries but rather to interests and interactions, and during our meetings we discovered some important relationships between organic farming movements in Sri Lanka and other organizations, including the Department of Export Agriculture.
FrontlineSMS Survey Results: Can we build accessible software? Yes we can, say our users!
Here at FrontlineSMS, we love data. Like, a lot. If data had its own Facebook page, we’d ‘like’ it and if we took a picture with data out one night, we’d probably make it our profile picture. Data empowers, and we’re all about empowerment o/. In fact, to empower people is the why for the what we do. One thing we’re always wanting to know, of course, is how we are doing. Well we SMSed our friend data to find out – Welcome to the 2013 FrontlineSMS survey results post!
VNI Service Award Finalist Jimmie Ssena uses FrontlineSMS to Empower Rural Farmers in Uganda
Congratulations to Jimmie Ssena for being recognized as a finalist of the VNI Service Awards for his work with rural farmers using FrontlineSMS! Since its founding in 1997, the Nakaseke Telecentre has served as a knowledge portal for poor rural farmers in their district, working to use ICTs “for rural development, reduction of poverty and... a better livelihood of the rural poor.”
MfarmerSMS service links farmers to better markets in Nakaseke- Uganda
The MFarmer SMS service, a project of the Nakaseke Community Telecentre in Uganda, helps farmers in rural areas to connect with better markets. It encourages two-way feedback with farmers, buyers and agro-processors, and other service providers. The project is designed to help farmers access agricultural market price information and weather information through their mobile phones.
FrontlineSMS:Radio adds an Exciting Tool to the Mix at Rite FM, Ghana
Guest Post By Tully McLoughlin
By 6:30 in the morning Owuraku Asamoah is seated comfortably at the black microphone in the Rite FM studio in Ghana, headphones on, twin computer monitors glowing, a laptop by his side displaying his Facebook page, his cell phone gripped firmly in one hand. “And this is how we’ll start today’s edition of the Morning Ride, being produced by Nii Alarbi,” he begins. “Believe in your hearts that something wonderful is about to happen.”
Rite FM broadcasts on 90.1 FM and online at www.ritefmonline.org from the bustling, 20,000-resident town of Somanya in the Eastern Region of Ghana. It occupies a unique niche of the radio space here – a commercial station for agriculture and social development. It is not simply an outlet for agricultural extension, nor do its programs present the standard rigmarole of music, politics, and religion. The catchment area, which includes portions of the urban Greater Accra region and large swaths of rural area in the Eastern and Volta regions, symbolizes that dual-demographic challenge.
I’m volunteering my time at Rite FM. I met the director of the station through their close partnership with Farm Radio International, an NGO with whom I work. Farm Radio was started in the late 1970s by a Canadian agricultural broadcaster who saw the need for better farmer-focused radio in Africa. The organization has been supporting commercial, public, and community stations on the continent since then, and in 2007 undertook the 42-month “African Farm Radio Research Initiative” with the support of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Rite FM was one of five Ghanaian stations in the project.
My phone buzzes on the table by my bed, waking me up. “Tully. Owuraku wants you to talk about the Africa’s Voices project on the Morning Show in one minute.” That’s Kofi Baah, called Granpaa, the show’s producer. It’s July 20th, 7 am. Asamoah is devoting today’s show to a discussion of food security in Ghana, inspired by this month’s question for the project. The Africa’s Voices project is being undertaken jointly by the teams at FrontlineSMS:Radio and the Centre of Governance and Human Rights at Cambridge University UK, and Asamoah is taking the opportunity to cover the issue.
The question asks: “According to you, which is the bigger threat to food security in your area?” The options are: climate change, land access, market access, and food prices. I explain that by texting in their opinion they stand to win a remote-control, solar-powered, two-in-one lantern radio. A perfect way for farmers, in the field and off the grid, to tune in, the station’s director had told me the day before.
Asamoah takes calls and guides the conversation as it drifts from a debate on industrialized farming techniques to genetically modified foods. He is a pro at making the programming interactive. Beyond his demeanor, he has a number of tools at his disposal. There are two phone-in lines; an additional four lines on the Freedom Fone, an Interactive Voice Response tool; and an all-network SMS short code provided by the SIIMA system of SMS GH, a SMS-solutions company in Ghana. In addition, Rite FM operates its own website. And of course there is the battery of social outlets: a Facebook and user profile (ritefm), and a twitter feed (@rite901fm), and various satellite websites for other Rite FM projects. Now, the introduction of FrontlineSMS:Radio as part of the trial adds another exciting tool to the mix.
The advantage of this arsenal is that listeners participate and hosts facilitate in the way they’re most comfortable. Callers pepper the Morning Show, which runs from 6:30 to 9am, and The Drive, which runs from 2 to 5:30pm. But for shorter programs like Time With the CEO, profiling senior executives of agricultural businesses to showcase models of success and affluence along the agricultural value chain, and Women in Agriculture, focusing on the role of women as wives, mothers, traders, and entrepreneurs, the host may not be seeking a spread of opinions.
SMS, and to some extent Facebook or Twitter, give the host the flexibility to incorporate certain comments fluidly. That means, Asamoah points out, “Even when I’ve not gone on air, I can respond to you.” For listeners, says Nii Alarbi, a reporter and broadcaster for the Rite FM news team, SMS may be the only way they will contribute. “It’s not everybody who will like to call in for other listeners to hear his or her voice.” On a good day, a producer might expect to receive 10 or so texts in a show.
Even when the number of outlets to interact with listeners feels overwhelming, Asamoah sees that running in the opposite direction isn’t an option. “If you stick to only phone-in, you can’t progress. You can’t reach out to everybody.” Alarbi, who also hosts Herbs & Spices and the Agricultural Forum, says the day he does a show without taking any input, he will think, “Maybe I did it to my satisfaction, but I left my listeners behind.”
To find out more about Cambridge University's Centre of Governance and Human Rights "Africa's Voices" project click here and to learn about other projects using SMS with radio, visit FrontlineSMS:Radio's website.
Catholic Relief Services uses FrontlineSMS to save Cassava Farming in Eastern Africa
A joint guest blog by FrontlineSMS and CRS manager Peter Mureith Climate change has severely affected the growth and production of crops on a global scale. Food security is a serious concern in many parts of Africa and Asia, and with a lower-than-expected yield in the US, unusually high rainfall in Europe and drought in the Horn of Africa, global food prices are expected to spike again in the coming year.
Catholic Relief Service (CRS) has long been using FrontlineSMS to work with communities in Eastern Africa – Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Congo, Rwanda and Burundi - to support alternative ways to improve cassava farming. Cassava is a staple food in the region, with its stem, leaves and root all being put to use. In Congo, the average family consumes 5kg of cassava flour and 3kg of its leaves every day.
In the past, with higher rainfall and fewer destructive crop diseases, cassava farming was profitable and fed farmers' families. In fact, it took only 3 months to plant and harvest the cassava tubal and its leaves. Today, farming has become more challenging and costly. Lower than average rainfall and new crop diseases have reduced crop yields. Many peasant farmers have changed professions to labor-intensive and dangerous jobs such as mining, exacerbating food shortages. With lower incomes, families struggle to send their children to school and provide sufficient food, suitable housing and basic health care.
CRS began working with communities to address these problems and help alleviate food insecurity in the region. The Great Lakes Cassava Initiative (GLCI) works with 1.15 million farmers, researching best practices on curbing cassava crop diseases and working to create a seed tolerant to diseases and drought. GLCI worked through partners in each district to distribute seeds which would thrive in that specific area. Through research, GLCI discovered that isolating a cassava plant which has been affected with the new crop diseases wasn’t the solution – the problem would return if its seeds were replanted and would affect other neighboring farms. GLCI worked to build awareness and provide tools and skills that would lead to positive action among communities.
58 partners and 250 staff with 250 laptops were an essential part of the GLCI implementation strategy. CRS used FrontlineSMS to enhance their communication, ICT strategy and data collection, and assist communication with partners. Many were in very remote areas where Internet access would be unpractical, unreliable and expensive. CRS used FrontlineSMS to send reminders, schedules on training opportunities, deadlines, announcements and collect data. CRS also applied a troubleshooting solution to handle computer errors partners would encounter. Staff would simply SMS their problem to CRS and CRS would respond with a solution, via SMS.
Through GLCI, farmers increased their yield, increased their income and improved their livelihood; a positive impact that had a ripple effect to the region's economy and its food security. In one instance, a GLCI farmer* in Tanzania was able to improve his yield and income and as a result, was able to increase contributions to his saving scheme, which afforded him financial freedom to increase his farm from 0.25 acres in 2003 to 30 acres now. He is also the main distributor of cassava seeds in three main districts.
*name withheld due to confidentiality and third party rights
Data Collected via FrontlineSMS is used by Ministry of Agriculture in Cambodia
In this guest post new FrontlineSMS user, Sophie Baron, shares how she is currently using FrontlineSMS in a pilot study to monitor and contain the spread of animal diseases in Cambodia. This pilot was initiated by Dr. Flavie Goutard and Dr. Sebastien Le Bel from the Centre de Coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement (CIRAD) and the Institut Pasteur du Cambodge (IPC). It is now providing valuable information to the Cambodian Ministry of Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries, through their National Veterinary Research Institute (NaVRI) at the Department of Animal Health and Production. In this post Sophie explains how the pilot has been set-up to overcome communications challenges, and discusses how FrontlineSMS is helping enable successful tracking and containment of animal diseases. By Sophie Baron
Infectious animal diseases are a major threat for the agricultural community in Cambodia. If levels of animal diseases are not monitored and contained effectively, this can have a negative impact on farmer’s livelihoods. I am working through the CIRAD, alongside IPC and NaVRI, to implement a targeted monitoring and surveillance system for animals. A pilot study is currently being implemented in two rural Cambodian provinces - Kampong Cham and Takeo. The sample for this pilot study is made up of 10 villages from each of 3 districts in both provinces; making a total of 60 villages. From each of the 60 villages, we asked the village chief and a selected village animal health worker (VAHW) to report the number of dead cattle, chickens, ducks and pigs in their village on a weekly basis. They were also asked to report the number of cattle infected by Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and Hemorrhagic Septicemia (HS); and the number of cattle that died from these infections.
The data reported via SMS by village chiefs and VAHWs helps to provide a more accurate baseline of animal mortality, and serves to alert NaVRI when mortality is higher than usual. If the reports being sent indicate that mortality is high, someone from NaVRI is sent to the relevant village to take samples from the animals, which are used to diagnose the condition. Based on this diagnosis appropriate actions are taken which curb the potential for an outbreak. Receiving regular data via SMS - and being able to manage this data within FrontlineSMS - helps enable NaVRI to adopt more timely and effective response mechanisms to breakouts of animal diseases.
When we were designing the pilot study, there were some interesting challenges that we had to consider. The pilot was targeting rural areas where access to internet is slow, so we had to build a solution that was accessible. Luckily, most people have mobile phones in these rural areas, but there is also a low usage rate of SMS in Cambodia. This is partly because phones do not support Khmer characters – which is the official language in Cambodia - making texting very difficult, and in some cases impossible. In addition, a phone call costs approximately the same as an SMS in Cambodia, thus reducing the incentive to communicate via SMS.
However, the high access to mobile phones means that SMS still offers a viable solution and enables effective data collection; we just had to be aware to design our use of SMS to suit the context. To get around the language challenge, we implemented a numbering system so that users just had to submit reports via SMS using numerical values as opposed to sending fully written text messages. We went to the villages and offered personal training to those who would be submitting reports via SMS, and further explained and documented the numbering system. In order to incentivize people to send their SMS reports the cost of SMS is reimbursed. On a monthly basis, VAHWs and village chiefs are given sufficient mobile top-up to be able to send SMS reports throughout the month.
The way we have designed the pilot seems to be working well. In the first few weeks, there was a 90% rate of response from the VAHWs. We have experienced some initial errors in the report format, but Ms. Kunthy Nguon, research assistant at IPC was able to call to follow up and clarify any incorrect reports, and to inform those reporting of the correct way to structure the content.
Since the pilot has proved efficient in helping us to receive timely and accurate reports so far, I have recently installed FrontlineSMS at NaVRI, where reports will continue to be monitored. The pilot started in February 2012 and will continue as a pilot study until June 2012. Following this point, we will evaluate the success of our use of FrontlineSMS and we will be looking for funding to continue the project from June 2012 and to expand into additional provinces.
Under the supervision of Dr. Arnaud Tarantola, head of the Epidemiology and Public Health unit at IPC, we are also currently reviewing ways that FrontlineSMS can be used in some other IPC projects, for tasks such as monitoring success of patient vaccination and collecting patient feedback. It has been really valuable to investigate the different potential uses of FrontlineSMS across public and animal healthcare, and we hope to expand use of the software moving forward. Sophie Baron is a veterinarian doing a Masters in Public Health, and specializing on epidemiologic surveillance of human and animal diseases. Thanks to a Fondation Pierre Ledoux scholarship, Sophie is doing a six month internship based at Institut Pasteur du Cambodge (IPC) as part of her studies.
Get the Word Out: Using SMS to Support Harm Reduction for Vulnerable Women
Guest post from FrontlineSMS user Gordon Gow, University of Alberta Here at the University of Alberta we are using FrontlineSMS to support graduate student research in communication and technology. Among its range of activities, the Mobile Applications for Research Support (MARS) Lab provides access to FrontlineSMS and mobile phones to allow students and community groups to set up and run pilot projects using text messaging.
Among our projects, the MARS Lab is providing support for “Get the Word Out” program operated in partnership with Edmonton’s Centre to End All Sexual Exploitation (CEASE). CEASE works through partnerships to create and pursue strategies to address sexual exploitation and the harms created by prostitution. Their work includes public education, client support, bursaries, counselling, trauma recovery and emergency poverty relief for individuals working to heal and rebuild their lives after experiencing exploitation.
“Get the Word Out” is a harm reduction service that uses FrontlineSMS to enable women involved in prostitution to anonymously report incidents or concerns about violence or crime that is affecting them or may affect others. The program also offers an network for these women to share thoughts or provide peer-based social support using anonymous text messages. FrontlineSMS is set up to auto-forward incoming text messages to a distribution group that includes frontline support agencies and clients who have chosen to subscribe to the service. The auto-forwarding process removes the callerID from the text and preserves only the contents, ensuring anonymity of the issuer. Text messages are also forwarded to a set of email addresses provided by the frontline agencies, as well as a protected Twitter account.
The MARS Lab is also involved in other projects using FrontlineSMS. For example, it is working in collaboration with Simon Fraser University to pioneering the use of FrontlineSMS in combination with Ushahidi to explore the use of social media in campus health and safety. This project is using FrontlineSMS to receive text messages from students and staff at both the University of Alberta and Simon Fraser University to report health and safety concerns on campus. The goal of the project is to better understand how text messaging can provide a low cost, low barrier means of reporting to encourage the campus community to help mitigate risks to health and safety on a university campus.
Furthermore, in early 2012 the MARS Lab will be launching a pilot project in partnership with LIRNEasia and the Sri Lanka Department of Agriculture to explore the use of text messaging to support Agricultural Extension Services in the Dambulla and Matale districts. This pilot will involve deployments of FrontlineSMS at three agricultural information centres and is also expected to include a deployment of FrontlineSMS:Radio with a local radio station to support audience interaction for one of the live agriculture talk shows.
It's great to see the diverse range of projects which the University of Alberta is supporting in their use of FrontlineSMS! This post was originally shared on the FrontlineSMS Community Forum. You can see the full original post and connect with Gordon on our forum here.
New radio documentary shows how FrontlineSMS connects farmers in Kenya
em>Clare Salisbury has recently completed her MA in multimedia broadcast journalism at the University College Falmouth, Cornwall, UK, and this summer has been making a radio documentary on the impact which technology is having on administering aid in Africa. Clare is particularly interested in the ways that mobile and internet technology are influencing small scale farmers, food producers and NGOs. She recently met up with some FrontlineSMS users in Kenya, and in this guest post she shares some of her experiences.
“In the summer of 2011, I travelled to Kenya to make a multimedia documentary about the impact of mobile phone technology on farmers and NGOs that support them. Although I was prepared to see mobiles everywhere, driving from the airport into the city, I couldn’t believe the enormous billboards advertising mobile operators which lined the motorway. The next morning, I sat in a shopping mall in Nairobi and watched as people literally battled for space inside the nearest mobile phone store. People were even queuing to get in the door.
This is, of course, just another day in the capital. During my week in Kenya I would see that the real changes are happening in the hands of people based in rural areas. For these people, the possibilities opened up by access to a mobile handset are life changing.
Whilst in Nairobi I met John Cheburet who founded a radio programme in 2008 to complement the work of The Organic Farmer’s magazine and other outreach work. His programme focuses on agricultural techniques in a programme aired on two national radio stations.
John uses FrontlineSMS to manage the growing number of text messages he receives from the farmers who tune in every week. It’s a great tool as far as production goes; especially because he can send reminders to his listeners about upcoming programmes. John also admits that it’s a great way to think up content, for example– if he wants to make a programme on successful chicken farming techniques, he can easily find a farmer who’s working with chickens to interview by flicking through his SMS message inbox.
Click here to listen to John, of The Organic Farmer, speak about his use of FrontlineSMS.
Moreover, this feedback ensures his programmes are reactive to the opinions of the listeners which enriches his programme. ‘Farmers know things’, he told me, ‘for a radio programme to be interesting, there has to be a two way communication.’
But as I found out later in my trip, this conversation facilitated by FrontlineSMS is happening in more than just two directions. In Busia, a border town between Uganda and Kenya in the western region of the country, I met Emmanuel: a small scale dairy farmer who trains his peers and neighbors as part of the Send A Cow project.
He was carrying a copy of The Organic Farmer magazine. It turned out he never misses an installment of John’s radio programme on the Kenyan Broadcasting Corporation (KBC). I asked him whether he ever texts into the show. He said he does, and that through the programme, he has made contact with other small scale farmers across the country and exchanged many ideas and techniques.
Emmanuel had clearly been motivated by the success and potential of text messaging. He told me how he encourages all the farmers and he helps to train them to use SMS effectively. This encounter was fascinating and it showed me that whilst the concept of text messaging is a simple two way dialogue, combined with a powerful radio presence, the two way conversation is only the beginning. As John said to me back in Nairobi; when he is producing, he likes to imagine that as well as disseminating information on The Organic Farmer, he is really only contributing to a much bigger knowledge exchange throughout the farming community.
I learned during my trip that mobile phones are changing the future for the small scale farmers in Kenya. And the many potential benefits of mobile technology continue to be explored. Spending a day in Nairobi’s sophisticated iHub innovation space for the tech community offered me an enormously exciting insight into what mobile technology tools could be to come for farmers in Kenya and across Africa, too. As international infrastructure accelerates to accommodate the technology being developed, farmers in Africa are increasingly able to benefit.”
You can find Clare's full radio documentary, as well as more audio and photos from her trip on her website here: http://aidtwenty.wordpress.com/ If you are interested in the powerful combination of mobile and radio technologies check out our FrontlineSMS:Radio project website here: http://radio.frontlinesms.com/
Tanzanian farmers report improved yields via SMS
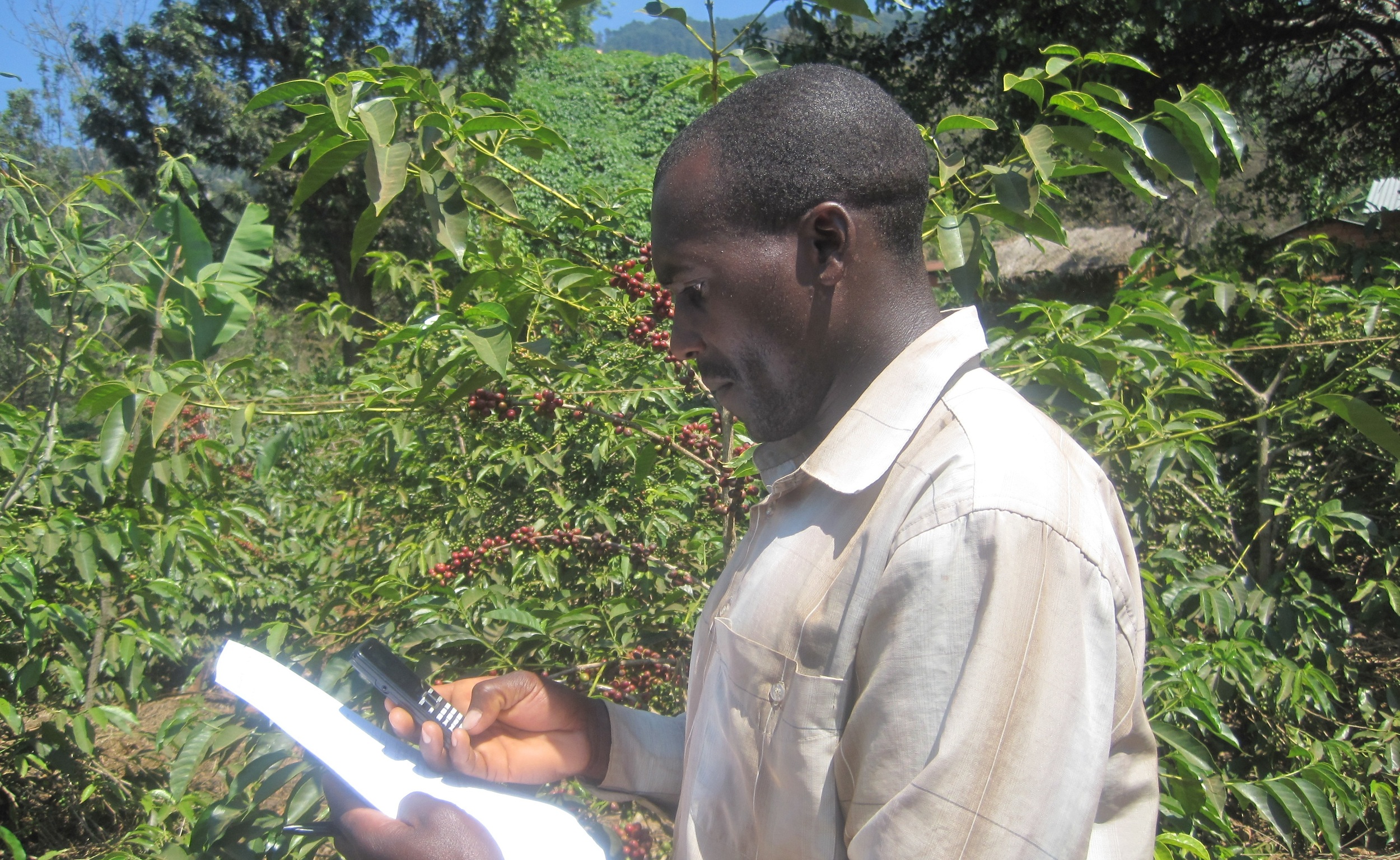 “Nearly 90 percent of Tanzania's residents live in rural areas, work primarily in the agricultural sector, and lack access to information, technology and markets,” Technoserve state on their website. Technoserve is an organisation which focuses its work in Tanzania on supporting farmers, cooperatives and suppliers in order to help develop rural industries. Whilst working towards these country-wide goals, keeping track of their impact is essential. Here, FrontlineSMS Community Support Coordinator, Florence Scialom, speaks with James Hangaya, Monitoring and Evaluation Analyst at Technoserve Tanzania, about how he is using FrontlineSMS to help collect the data he needs for monitoring Technoserve's Coffee Initiative project in Tanzania.
“Nearly 90 percent of Tanzania's residents live in rural areas, work primarily in the agricultural sector, and lack access to information, technology and markets,” Technoserve state on their website. Technoserve is an organisation which focuses its work in Tanzania on supporting farmers, cooperatives and suppliers in order to help develop rural industries. Whilst working towards these country-wide goals, keeping track of their impact is essential. Here, FrontlineSMS Community Support Coordinator, Florence Scialom, speaks with James Hangaya, Monitoring and Evaluation Analyst at Technoserve Tanzania, about how he is using FrontlineSMS to help collect the data he needs for monitoring Technoserve's Coffee Initiative project in Tanzania.
** This post has also been shared by Technoserve, and reported on by AllAfrica. **
Training for farmers is a key to Technoserve’s strategy in Tanzania, and forms a large part of their Coffee Initiative project. Training sessions help small-scale coffee farmers produce better quality coffee, thus helping them to secure higher prices in the international marketplace. “Sessions are based on different topics, and include practical lessons on, for example, how much fertilizer should be used to produce the best yield,” explains James. The farmer trainers hold multiple sessions on agricultural best practices, helping farmers to use their equipment and run their farming practice more efficiently.
One of the key steps in monitoring and evaluating the success of training is to measure the changes in farmers’ behaviour. “We train approximately 12,000 farmers every year” James tells me, “and there are nearly 60 farmer trainers across the country at the moment, running courses for groups of 15 to 20 farmers at a time.” There is certainly a lot of data to keep track of, and this is where FrontlineSMS proves very helpful Technoserve's work.
After experiencing the challenges of monitoring and evaluating their training programmes using extensive paper surveys, James and the Technoserve Tanzania team decided that there must be a more efficient way. This is when they came across FrontlineSMS data collection tool, FrontlineForms. Using this tool Technoserve farmer trainers are now able to conduct all post-training evaluation via SMS.
James explains how they manage this process: “Each farmer that attends a training session is allocated an individual ID. When filling out FrontlineForms, the farmer trainers use this ID to identify which individual farmer they are collecting data on. They answer set survey questions about farmer behaviour, using a pre-defined scale of 1-10 to indicate responses. They then send them back to me in the office to analyse the data.” This gives Technoserve Tanzania the data they need, to indicate whether the training has had an impact on the way the farmers manage their crops.
In addition, farmer trainers are provided with scales to measure a sample number of farmer’s harvest weights. These weights are compared with the farmer’s previous yield, and show how much farmers are able to produce before and after Technoserve training courses. Collecting these kind of direct indicators of impact is key to monitoring the success of the Coffee Initiative training sessions, and FrontlineForms is allowing this data collection process to be done much more quickly, and at a lower cost to Technoserve Tanzania.
The transition from paper to SMS has made a great difference to work flows, as James explains; “it saves us so much time and money, because our field staff no longer have to travel from the field to deliver paper survey results to our office, which can be a journey of more than 1,000 kilometres.”
This use of SMS technology makes the data collection process more efficient in error detection, too. As James says, “If I had picked up a potential error or if there was any data missing in a paper report then I would have to send it all the way back to the field to check whether the data needed to be edited; now I am able to this much more quickly and simply, via SMS.” These efficiency savings help to demonstrate the value of using FrontlineForms as a data collection tool.
Technoserve Tanzania plan to continue using FrontlineSMS for monitoring and evaluation, and are looking at ways to optimise and extend the ways they use the software, too. “In future we are looking to use FrontlineSMS to register farmers for training sessions and track their attendance. This will allow us to provide real-time reporting from the field,” explains James.
As Technoserve get accustomed to using SMS in their day to day work flows it is clear they are finding out more and more ways for it to help them make their work quicker, easier, and more efficient. James summed up this fact well by saying, “my boss agreed that we should change to FrontlineSMS for all the things that it can do for our work!”
You can find out more about what FrontlineSMS can be used for here, download the software for free here, and access FrontlineForms here.
“TechnoServe makes a commitment to businesses and industries, working in the field with entrepreneurs and other industry stakeholders to build enterprises able to thrive on their own and generate continuing benefits for the rural poor.” You can read more about their work on their website: www.technoserve.org
Climate Information Alerts for Poor Farmers
div>
This article was originally published on allAfrica.com and is reposted with permission.
There are few greater challenges facing rural farmers in the developing world today than climate change, as the current drought in the Horn of Africa demonstrates so clearly.
In this post, Riedner Mumbi and Polly Ghazi explain how mobile technology is being increasingly used to get crucial information out to poor farmers in Zambia, helping mitigate against climate risks and improving food security.

By Riedner Mumbi and Polly Ghazi
A herder shepherding his animals in Zambia’s Eastern Province winds up a solar-powered radio and crouches down to listen to a local FM station. The news broadcast includes a warning that a severe storm is approaching his village. The herder reacts instantly, finding shelter nearby for his animals, which later emerge from the storm unscathed.
Such a scene may be played out increasingly in the future across Africa, where the livelihoods of rural inhabitants are critically dependent on weather and climate. Most are peasant farmers who depend solely on rain for their crop production. A single extreme event such as a major flood or prolonged drought can not only cause loss of life, but also economic setbacks equivalent to years’ worth of development.
As climate change intensifies, bringing more extreme weather, as well as seasonal and longer-term changes, effective adaptation for rural regions of Africa will depend on timely and accurate advance information. Early warnings will enable farmers to shelter their animals and protect their income and families. In addition, the collection and distribution of local rainfall information can help smallholder farmers to adjust their crop production methods to changing seasonal precipitation patterns.
The Zambian government has been one of the first in Africa to recognize this need. Through its RANET (Radio and Internet for the Communication of Hydro-Meteorological Information) Project, the Zambia Meteorological Department is tapping remote communities across several provinces to collect climate information. In the past four years, some 3,060 farmers have been provided with rain gauges to take rainfall measurements which are then fed back to the meteorological service’s local weather stations through mobile phones. Farmers are also encouraged to report other local weather observations. To motivate farmers taking part, RANET periodically recharges their phones with free airtime, and project managers are now testing the FrontlineSMS software to help minimize the service cost. This would enable rural participants to send SMS – text messages – to the RANET centre free of charge.

The results have been so encouraging that the Zambian Met Office is now considering providing automatic weather stations and rudimentary meteorological training to rural farmer cooperatives across the country.
In order to help remote rural areas receive (as well as collect) timely weather and climate information, the RANET Project sends weather alerts via SMS text and has also been assisting rural areas to establish community FM broadcasting stations. These pick up regional climate information from satellites, translate relevant weather information into local languages and are then used to broadcast timely warnings over extreme weather, such as storms, as well as seasonal climate information.
So far the project has helped launch five stations, with two more in the pipeline, and is cooperating with another nine. Each station can broadcast information to farming communities within a radius of 40-60km. RANET has also installed 49 digital radio satellite receivers to enable the FM stations to access satellite-based weather and climate information.
The project provides communities with solar wind-up radio receivers to access the broadcasts, 3,000 of which have been distributed across rural regions to date. The stations also host programs that help educate citizens on the effects of weather on their crops. Reinforcing these messages, RANET also provides climate information to agricultural extension workers who can interpret it for farmers and help them apply what they learn in their daily farming activities. In Mali, similar weather forecast bulletins, broadcast every 10 days, have helped low income smallholder farmers to increase yields by providing vital information on when and what to plant, depending on the climatic conditions.
While community radio broadcasting struggles to survive commercially, and therefore depends on government and non-governmental organizations to sponsor their programs, this is worthwhile investment. Quite simply, radio broadcasting is the most cost-effective and cheapest way for information dissemination and education, and can play a valuable role in societies facing climatic extremes.
Not content with radio and cell phone networks, RANET, with support from the USAID Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance, is also piloting the deployment of an innovative communication device called Chatty Beetle. The device is both a terminal and a system designed to provide emergency weather alerts and instructions to remote locations with limited means of communication with the outside world. It sends messages and short status reports (of 160 characters or less) via a small screen between emergency managers and warning authorities, as well as notifying communities of potential hazards. Since speed is critical when warning vulnerable communities of the onset of disasters such as cyclones or major floods, the Chatty Beetle, which transmits even faster than the Internet, shows much promise.
With more than three quarters of the world’s population now served by mobile networks, and additional efforts underway to reach the rest, the RANET approach to climate and emergency preparedness information has huge potential for scale up.
Current RANET funding and technical partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), National Meteorological Services, First Voice International (formerly World Space Corporation), Free Play Foundation, UNDP, SNV, GTZ, DFID, World Vision, Africare, the Red Cross, and many others.
The World Resources Report 2010-2011 will be published in August and can be read here.
Riedner Mumbi is a consultant on the RANET system. Polly Ghazi is a writer and editor at the World Resources Institute (WRI).
Small-scale producers in Côte d'Ivoire manage international markets via SMS
The below is content from a FrontlineSMS Community Forum blog post, by FrontlineSMS user Julien Gonnet.

RONGEAD is a non profit organisation in Côte d'Ivoire which helps facilitate small producers in Africa to gain better access to markets. In Côte d'Ivoire they transmit information on the cashew market via SMS. This is a big job, considering Cote d'Ivoire is the second largest exporter of raw cashews, generating incomes for approximately 250,000 producers. RONGEAD are regularly in contact with producers of cashews in five regions of the country, and they use FrontlineSMS to send 3,000 SMS every week providing up to date information on market prices. In addition they provide valuable training and educational materials.
Julien Gonnet, of RONGEAD, recently shared details on our FrontlineSMS community forum about how they have set up a project to enable more than 8000 producers and 250 peasant leaders to have access to the information, tools, knowledge and skills which can help to enhance and secure revenue sources. The project involves "creation of a proactive network of shared knowledge of the world market for cashew value chain in Cote d'Ivoire."
This project has thus far provided five training modules for the producers and peasant leaders. The training modules address particular descriptions of the industry (covering main actors and relationships), an explanation for the formation and evolution of the price (including information on changes in supply and demand), and guidance on market decision making, such as when to sell and how to store goods effectively. A dozen educational materials - as shown in images here - have been developed during the project, including a role play!
At the level of information dissemination, each week, a market analysis is performed by relevant two specialists in the sector in Côte d'Ivoire and France. These summaries are released in a variety of ways, including as an electronic newsletter, though local radio and through 3000 SMS, differentiated by region, sent each week by FrontlineSMS.
This RONGEAD project has caused a great excitement, by providing accessible to information and training. Plus it has helped create relationships of solidarity between local producers. In the past relationships have been diminished following the stigma affecting certain cooperatives, and the climate of suspicion within a sector perceived as opaque and unstructured. Therefore, it is good to find positive projects which counteract this.
Julien points out that the objective of RONGEAD's project is not "simply to disseminate collected prices, but add elements of market understanding." As he explains "it is necessary to assist producers receiving the information to promote their own decision making and avoid counter-productive misunderstandings."
To learn more about the work of RONGEAD visit their website: http://www.rongead.org
Please feel free to join the FrontlineSMS Community Forum to connect with other FrontlineSMS users, and share details of how you are using FrontlineSMS too!
“Farming Out” Agricultural Advice Through Radio and SMS
This post is the latest in the FrontlineSMS Mobile Message series with National Geographic. To read a summary of the Mobile Message series click here. Amy O'Donnell, Project Manager, FrontlineSMS:Radio
The Organic Farmer, a Kenyan magazine about ecologically friendly farming practices, recently launched two radio shows aimed at smallholder farmers. John Cheburet is spearheading the use of FrontlineSMS on the radio shows, and, as Project Manager of FrontlineSMS:Radio, I was keen to speak with him. Radio represents the dominant media source for many people worldwide and it offers a vital tool for outreach, particularly to rural communities. FrontlineSMS:Radio works with community stations to discover how combining mobile phone technology with radio can engage listening audiences.
John Cheburet is a radio producer and a pioneer, offering a farmer information service for small-scale farmers and actively seeking new technologies to improve outreach. He is seen by the farming community as a friendly source of information which is vital for their livelihoods. While The Organic Farmer (TOF) was born as a print medium, John sees radio as a way to increase awareness and reach more farmers.
John’s listeners own an average of 2.5 acres. Many farm for subsistence and sell surplus to cover household needs and also pay school fees for their children. They may not have received training or know about the latest technologies, and they seek access to solutions and advice."
“In Kenya, agriculture is the mainstay of the economy and the population depends on the land both directly and indirectly. The country is a major exporter of tea and coffee, and 70% of the workforce is in agriculture and areas that service this sector.”