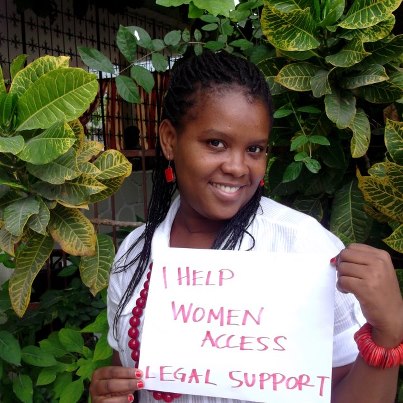Pandemics have a classic hallmark; they cause widespread uneasiness and unrest when they hit and the ripple effects can still be felt in their wake. During this period of uncertainty, lack of coherent messaging targeting communities springs up misinformation, rendering prevention and mitigation efforts futile and chaotic.
DataAid: managing information streams in the Philippines disaster response with FrontlineCloud
Over the past couple years, I’ve had the privilege of co-managing World Vision’s Speed Evidence Project, which seeks to improve information management in the immediate aftermath of a disaster. After most disasters, reliable field data is significant challenge - what we can find is normally incomplete and/or inaccurate.
FrontlineSMS in the Philippines and the Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda) response
FIRST Response Radio - Life Saving Information in Disaster
A big thank you to Mike Adams, the INTL Coordinator, for sharing his experiences with FrontlineSMS and further schooling us on how radio can facilitate in saving lives! In times of disaster radio not only saves lives, it can also bring hope and critical information to the affected community. When the 2004 tsunami struck Banda Aceh, Indonesia, all the radio and TV stations went off air. Similarly, during the 2005 South Asian earthquake, the only radio station near the epicentre lost its tower and went off air. In times like these, people are in desperate need of news and information on how to get to safety and how to survive. However, the unfortunate trend seen recently is that when radio is so important, many times it goes off the air and does not come back until well after the emergency is over.
Can Citizen Journalism Move Beyond Crisis Reporting in Traditional Newsrooms?
Citizen reporters broke much of the news, though they still needed broadcast media to help spread it. In some cases, citizens were able to capture iconic photos of events. Others were able to tell compelling stories about how the emergency affected their lives, including obeying the "stay in place" request by government officials during the manhunt. It has been widely reported how quickly social communities also got information wrong, including falsely accusing suspects. But I've seen a nearly equal number of reports showing how quickly these communities were able to self-correct their own misinformation.
Keeping it Simple with SMS
UN Special Envoy to the Western Sahara Christopher Ross landed in Morocco last Wednesday. While the international community anxiously waits to see where his next round of negotiations go, here's a peek into the lives of those affected most by the outcome - Sahrawi refugees. For once, a little hope for the future coming from the Sahara...
FrontlineSMSat7: KOFAVIV Supporting Haitian Women
In the fourth of our seven blog posts celebrating the month that FrontlineSMS turns 7, Sean Martin McDonald, CEO of our social enterprise, reflects on howKOFAVIV, a women's organization in Port-Au-Prince, supports women affected by rape and domestic violence via SMS, in the aftermath of the 2010 Haitian Earthquake.
"My favorite thing about working at FrontlineSMS is just how commonly we’re exposed to people doing inspirational things to make their communities stronger. I don’t know that I’ve ever been to a community that has needed more strength than Port-Au-Prince in the aftermath of the Haitian earthquake.
Amidst crushed concrete and the desperation of the tent camps, there’s an organization called KOFAVIV that has built a haven amidst the chaos. KOFAVIV is a network of women and men who reach into the often dangerous, neglected neighborhoods of Port-Au-Prince to extend a helping hand to victims of sexual violence in the moments when they need it most. KOFAVIV connects victims to healthcare, legal representation, and, most importantly, community, giving them a voice and a way forward. KOFAVIV was started by victims of rape who are now changing what it means to be a victim.
"In Spring of 2011, the women of KOFAVIV allowed me to stay with them for a few days, observing their work and contributing a few ideas about how FrontlineSMS could be used to improve coordination. The organization has used FrontlineSMS to organize gatherings, send urgent security alerts, and manage their network of agents.
"It’s easy to talk about communication; it’s hard and dangerous to see it done so well. When I celebrate FrontlineSMS and think of the things that we’ve accomplished over the last 7 years, my proudest moments are when I get to see how we’ve contributed, in the tiniest way possible, to the incredible feats of human courage and compassion enacted every single day by the women of KOFAVIV and the organizations like them."
We’re collecting photos of our users telling the world how they use FrontlineSMS. If you want to get in on the act, take a photo of yourself or your team holding a piece of paper or a whiteboard telling the world what you do with FrontlineSMS. For example: ‘I monitor elections’, ‘I safeguard children’ or ‘I make art’. You can see a slideshow of the photos we’ve had so far on our Flickr page.
It doesn’t matter what language it’s in as long as it’s legible and if possible you should be able to see from the photo where it was taken, so, if you can, get out of the office!
You can: - post to Twitter or Instagram with the hashtag #FrontlineSMSat7 - email the picture and we’ll post them - post the picture on our Ning network and we’ll post them - post them on Flickr or any other web service and let us know where they are
Sending a Message of Accountability: SMS Helps Improve Services After Pakistan Floods
In this guest post, Alex Gilchrist explains how the Popular Engagement Policy Lab (PEPL) used SMS to communicate with affected communities during the humanitarian response to the floods in Pakistan in 2011. Using FrontlineSMS to set up a Complaints and Response Mechanism, people were able to share their experiences of accessing food and shelter. Co-authored by Syed Azhar Shah from Raabta Consultants, this post demonstrates how it is through the effective use of communications technology that people can be connected to the services they need the most. Guest Post by Alex Gilchrist, Popular Engagement Policy Lab and Syed Azhar Shah, Raabta Consultants
The 2011 monsoon flooding in Sindh, Pakistan’s southernmost province, affected an estimated 5.5 million people. The floods compounded the damage caused by flooding in 2010 and the lack of clean drinking water, food, healthcare and shelter resulted in communicable and non-communicable diseases across the province. It also caused loss of livelihoods through damage to agricultural land and death of livestock that will continue to affect the lives of the people of Sindh for years to come.
In the aftermath of the recent flooding, a large Pakistani NGO called Strengthening Participatory Organisation (SPO), which manages a network of organizations across Sindh province started a new project in Mirpur Khas district, distributing food items and shelter to those worse affected. Following an assessment process for one of its smaller projects, SPO selected a total of 475 beneficiaries across 24 villages.
A concern of SPO’s head office in Islamabad was that complaints and feedback from beneficiaries in previous projects had not been documented or dealt with effectively and they wanted to monitor the distribution process. This is when the Popular Engagement Policy Lab (PEPL) and Raabta Consultants were asked to help.
We were asked to set up a mechanism through which people could register issues they encountered during the flood relief distribution project in order to improve accountability and transparency before, during and after the distribution had taken place. PEPL develop research methodologies, specializing in innovative uses of low- and high-tech information systems, and for this project we collaborated with Raabta Consultants, who help communities in Pakistan to access the valuable social services provided by governments, NGOs, charities and the private sector. Using FrontlineSMS, we developed a system to handle SMS-based feedback from affected communities as part of their new Complaints and Response Mechanism (CRM).
Although less than half of Pakistan’s population owns a mobile handset, recent research indicates that more than 70 percent of people have regular access to a mobile phone. Amongst phone owners in the poorest 60 percent of Pakistan’s population, 51 percent of men and 33 percent of women used SMS, according to a survey by LIRNEasi in 2009. We wanted to test whether we could harness the prevalence of mobiles and the use of SMS for improved accountability.
Beneficiaries of the project were selected in virtue of being the most disadvantaged in each village: often those with disabilities; child-headed households; or female-headed households, and literacy rates among them were low. We realized it would be a challenge to design a system that would be accessible and useful across the board. To put these concerns to the test, we conducted a questionnaire involving participants of both genders on mobile phone usage. To the surprise of the project team the overwhelming response was that access to mobile phones was widespread, and if someone did not own a mobile phone then they could borrow one from a family member, friend or even village council member and even ask someone to write a message on their behalf. Through this evidence about the culture of using mobile, we gained overwhelming support for a system to base the CRM on a combination of text messages and voice calls.
The next step was to configure a system using FrontlineSMS so that people could text us requesting a call back. Sindhi is largely written in Arabic text, but not all handsets can recognize the Unicode in which it appears. So, following the conversations with villagers, the team devised a numbering system for complaints ranging from 1-0. The code was as follows: 1 = Food items, 2 = Shelter, 3 = Conflict 4 = Corruption, 5 = Issues with SPO staff, 6 = Issues with Partner Organisation staff, 7 = Issues with Village Council, 8 = Issues affecting women and children, 9 = Issues affecting those with disabilities, and 0 as a means of saying “thank you”. This numbering system allowed for automatic replies through FrontlineSMS tailored to the complaint, as well as a response time.
The numbering system was printed on cards with corresponding pictures, and the SMS and feedback system was also explained through diagrams. On the cards we included telephone numbers for verbal complaints and instructions for written complaints. Having printed out leaflets, posters and cards the teams went to every village and explained the process to beneficiaries and non-beneficiaries alike. During this process, field workers documented all beneficiary phone numbers or relatives’ and friends’ phone numbers, which were then saved in FrontlineSMS. This meant that every message received in FrontlineSMS would also have a name attached to it, and the system was set up so that every auto reply contained the name of the sender. We believe that the in-person relationship is a critical step that makes the difference in the popular uptake of a communications system.
Through the groups feature on FrontlineSMS, we created lists for village and Union Council members so that before each aid distribution process SPO could send messages alerting the beneficiaries about its arrival, and following the distribution process we could actively solicit feedback via SMS. When a message was received, the response manager would call back, ask for more information and then follow the internal complaints procedure.
Over the three-month aid distribution project we received 725 messages, 456 of which followed the numbering system. The awareness of this system amongst partner organizations and project staff meant that they knew they were being held to account for their actions, so it ensured the quality of their work. It was especially important that the system protected the identity and data of participants in a way that could not be tampered with. Fundamentally, we learnt that giving people a direct means with which to register a complaint or feedback empowered the beneficiaries of the relief effort to have a say in the way they were treated and furthermore to be connected with organizations who could offer further support.
Faster Channels of Communication: A Radio and SMS Initiative in NE Kenya
The objective of Infoasaid - a consortium of Internews and the BBC World Service Trust - is to improve how aid agencies communicate with disaster-affected communities. The emphasis is on the need to deliver information, as aid itself, through the most appropriate channels. You can read more about Infoasaid's work on their website http://infoasaid.org/
The article is republished below with permission, or read the original post here.
Infoasaid has helped Save the Children to improve its two-way communication with half a million drought-affected people in Northeast Kenya.
The project uses mobile telecommunications and community radio to establish new and faster channels of communication between the aid agency and remote rural communities.It was launched in Wajir County, close to the Somali border, in the fourth quarter of 2011 and will run during the first six months of 2012.
Save the Children runs vital health, nutrition and food security projects in Wajir County, a semi-arid region which has been devastated by three years of drought and serious food shortages. Its operational centres in Wajir and Habaswein will use SMS messages to exchange information with health workers, relief committee members and community representatives in outlying areas.
Save the Children will also sponsor special programmes on Wajir Community Radio, the local radio station. The radio station broadcasts in Somali, the main language spoken by local people. It commands a large and loyal audience within 150 km radius of Wajir town.
Most people in Northeast Kenya are semi-nomadic pastoralists. They depend on their herds of camels, cows, sheep and goats to feed their families and generate a small cash income. Infoasaid therefore set up weekly radio programmes that will inform local people about the latest animal prices and market trends in the area’s two main livestock markets; Wajir and Habaswein.
It also helped Save the Children to design a weekly magazine programme on Wajir Community Radio. This will focus on key issues related to the aid agency’s emergency aid programmes in the area. The radio programmes, which include a phone-in segment, will focus on issues such as health, education and food security and alternative livelihoods.
The mobile phone element of the project will establish FrontlineSMS hubs at the Save the Children offices in Wajir and Habaswein. FrontlineSMS is free open source software that turns an ordinary computer into a text messaging exchange.It will enable Save the Children to broadcast SMS messages simultaneously from the computer to a variety of different contact groups in the field.
Each message is drafted on the computer, which then uses the FrontlineSMS software to send it by SMS to a large group of recipients.In this way, the same short message can be sent rapidly to a group of 50 or more people through a simple operation that takes less than two minutes to perform.
Previously, Save the Children staff would have had to telephone or visit each of the targeted individuals personally to deliver the same message. That process could have taken several days to complete
The FrontlineSMS hubs in Wajir and Habaswein will not only send out vital information. They will also capture and record incoming messages from people in the field. Each incoming message will be evaluated immediately and passed on to the appropriate person for a timely response.
Infoasaid supplied 240 basic mobile handsets and solar chargers to facilitate the establishment of these two SMS messaging networks. The equipment is being distributed to collaborators and community representatives in every location where Save the Children provides local services.
To read the original article please click here.
Supporting disaster affected communities in Haiti using FrontlineSMS
Guest post from Andy Chaggar, Executive Director of European Disaster Volunteers (EDV) who are using FrontlineSMS in Haiti:
European Disaster Volunteers' mission is to help disaster affected communities worldwide achieve sustainable recovery. This means doing more than simply addressing the damage caused by disasters; it also means addressing the underlying, long-term factors that made communities vulnerable in the first place.
We’ve been working in Port-au-Prince, Haiti since June 2010 and have placed a high priority on education since the beginning. EDV has rebuilt or repaired 36 classrooms in eight schools, are providing scholarships to 50 primary school children, and also run free English classes for adults.
Having originally graduated with a degree in electronic engineering in 1999, this work is a major change in direction for me. However, given my previous career it’s probably not surprising that I’ve retained a strong interest in technology, particularly in its application to disasters and development. So, when I heard about FrontlineSMS, I immediately saw its usefulness to EDV’s current work in Haiti.
From the outset I knew FrontlineSMS would be particularly helpful for our English Education program. English is a key vocational skill for Haitians seeking employment and, almost as soon as we arrived, we started getting requests from our community for language support. Over the past 17 months, what began as informal classes has developed into a structured program that includes 120 students in eight weekly classes at four different levels.
Managing communications in the program was a challenge from the outset. In addition to the students, we have to coordinate our Haitian teachers and international volunteers. Everyone needs to be kept informed of the time and location of meetings and scheduled classes are prone to disruption.
In a country like Haiti, everyday issues like teachers being ill are compounded by problems of instability. Potential hurricanes, political unrest or simply a particularly heavy rainstorm all have the ability to disrupt class, so the ability to communicate is vital.
Very few Haitians have regular access to the Internet so group emails aren’t an option. Before using FrontlineSMS, we would often have to scramble to call, or text, everyone affected to reschedule a class. In some cases, such as during heavy rain, an unlucky volunteer would have to walk to a class where we knew very few students would turn up simply to apologise to the few who did and tell them to try again next time.
Now, by using the software’s ability to create contact groups, we can very quickly and cheaply text all students in a given class or call all of our Haitian teachers in for a meeting.
Our English program is very popular and also has a big waiting list. When spots in our various classes recently opened up, we were also able to use FrontlineSMS to text over 100 prospective students and invite them to take a placement test so we could fill the classes with students at the right level.
Overall, this simple but effective technology has made managing our English Program much easier. Without FrontlineSMS, we would still be using chaotic, time-consuming and inefficient methods of communicating, all of which would distract and disrupt the actual work of teaching.
The fact that FrontlineSMS is free is also very appealing to us. While we’re a growing charity, we’re still fairly small and love to save money by using free technology. Beyond this, however, an important principle is at stake. EDV is committed to working with disaster survivors to build local capacity to meet local needs. This partly means connecting survivors with tools they can use themselves. Even if we could afford to buy expensive, licensed software, the survivors we work with never could. As a result, we always prefer to use technology that is as accessible to survivors as it is to us.
We’re in the process of handing over leadership of the English Program to our local teachers and a Haitian school administrator. As part of this process, we’ll be providing a computer with the software and contact groups installed so that our communications solution is transferred. We’ve found using FrontlineSMS to be very intuitive so we’re confident our school administrator will continue to retain and develop use of the technology.
We have other future plans for use of FrontlineSMS in addition to our English Program, and see many ways it can help us operate more effectively. We currently also use the technology for our own internal messaging which is critical in Haiti due to security issues. Political demonstrations can be dangerous and can happen with little warning, so being able to quickly text all of our in-country volunteers and tell them to return to base immediately helps keep everyone safe.
We’ll definitely continue to use FrontlineSMS internally in other disaster zones, and we will continue to explore other potential project-related applications for the technology as well. For example, a couple of years ago I visited a community group in the Philippines who provided early warning alerts to its members living in typhoon and flood prone areas of Manila. While doing an amazing job, they were reliant on an aging infrastructure of radios and loudspeakers and this process could have been strengthened using FrontlineSMS.
I see the need for such early warning systems time and time again and I’m fairly confident that in the future such work could be complemented and improved by using FrontlineSMS to quickly text those in danger. Moving forward, I’m excited to see how FrontlineSMS, and technology overall, can be applied to solve important real-world challenges and both help to save and improve lives.
UN uses FrontlineSMS to help manage aid response in East Africa
em>By Lisa LaRochelle, FrontlineSMS Project Assistant FrontlineSMS is being used for social change in many different ways across the world. Common use case examples include election monitoring, provision of health information, and agricultural support – these kinds of use cases have direct positive impact on people’s lives. Yet here at FrontlineSMS we have seen increasing numbers using FrontlineSMS for organisational management, which has indirect benefits for people which are
far harder to measure and demonstrate; helping organisations to work more efficiently, communicate more easily with their staff, and move information around more swiftly. Examples include using FrontlineSMS for monitoring and evaluation, data collection, and internal communication. It is this latter kind of FrontlineSMS use case that we recently discussed with Sanjay Rane, Information Management Officer at the United Nations Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) in Kenya.
Mobile phone penetration is high in Kenya, and the UN OCHA staff members that Sanjay works with all have their own mobile phones. The convenience and accessibility of SMS appealed to the team, and FrontlineSMS is a low-overhead way of managing text messages to and from groups. “For the last couple of months we have been using FrontlineSMS as an in-house communication tool,” Sanjay explains “and it has certainly helped foster better information sharing among the OCHA Kenya team.”
SMS offers an immediacy and intimacy that can be seen as unique from other methods of communication. People always have their mobiles close to them, and generally read messages quickly. This has certainly shown to be the case in OCHA’s experience. They have found that using SMS helped them to reach staff, especially during an emergency occurring in off hours, when most of the staff do not check their emails. OCHA Kenya can use the tool to send out urgent updates to the team.
One of the major benefits of using FrontlineSMS is the ability to manage SMS more easily than using a simple phone handset. When trying to send out messages using a handset, Sanjay found it difficult and time consuming to add and delete people’s contact information, send messages to multiple contacts at the same time, and maintain groups of contacts. FrontlineSMS offers a simpler solution: the ability to sort contacts into groups so that, for example, an emergency alert text can be sent out to a large group of staff at once. It is also possible to set up key words and automatic replies with FrontlineSMS, so the system can automatically send people important advice and information.
The OCHA Kenya team had such success with their experience that they decided to implement FrontlineSMS to facilitate communication with a larger group of humanitarian partners in Kenya, as a preparedness tool for the referendum in 2010. They are now exploring the possibility of using SMS to help coordinate with agencies responding to the current East Africa drought. This is an indication that FrontlineSMS is enabling improved communications management in a way that was otherwise not possible.
It was the capacity to manage data in combination with the popularity and simplicity of SMS which led Sanjay to FrontlineSMS. “At OCHA Kenya, using SMS for internal communication is very popular, as it is a familiar communications tool. We have found it really valuable to use SMS for communicating with colleagues on important humanitarian developments in Kenya,” Rane says. Organisational management, although behind the scenes, can provide huge social benefits by enabling those working for NGOs and INGOs to communicate more effectively and do their challenging jobs more efficiently
Combating food insecurity in Northern Kenya
a href="http://infoasaid.org/" target="_blank"> infoasaid is a consortium of Internews and the BBC World Service Trust. The objective is to improve how aid agencies communicate with disaster-affected communities - the focus is on providing humanitarian information. The emphasis is on the need to deliver information, as aid itself, through the most appropriate channels. In this guest blog post first published on their website, infoasaid highlight some of the innovating approaches they are piloting to using FrontlineSMS in communicating with communities affected by crisis.
** This use of FrontlineSMS has also been reported on by ActionAid, the BBC World Service Trust and ReliefWeb. In addition, we included it in our National Geographic blog series, Mobile Message. **
infoasaid is a consortium of Internews and the BBC World Service Trust. The objective is to improve how aid agencies communicate with disaster-affected communities - the focus is on providing humanitarian information. The emphasis is on the need to deliver information, as aid itself, through the most appropriate channels. In this guest blog post first published on their website, infoasaid highlight some of the innovating approaches they are piloting to using FrontlineSMS in communicating with communities affected by crisis.
** This use of FrontlineSMS has also been reported on by ActionAid, the BBC World Service Trust and ReliefWeb. In addition, we included it in our National Geographic blog series, Mobile Message. **
Targeted, reliable information can help save lives in crisis-affected communities. As famine is declared in neighbouring Somalia, we’re helping ActionAid to improve vital communication with drought-affected populations in northern Kenya.
Open source mobile solutions such as FrontlineSMS and Freedom Fone are enabling two-way communication with vulnerable communities.
A chronic problem
Isiolo County in north eastern Kenya suffers from chronic drought and food shortages. A population of about 143,000 mostly semi-nomadic pastoralists rely on their herds of camels, cattle, goats and sheep for daily food and much of their cash income.
Many of the communities in this semi-arid area have been continuously dependent on food aid from the World Food Program (WFP) since 2004. ActionAid has been heavily involved in both long term development and drought-response projects in the Isiolo area for more than 15 years.
It knows that better communication can help save lives.
Livestock information bulletin
 The BBC WST and partners Internews are collaborating through the “infoasaid” project to help ActionAid provide timely information to pastoralists, to help combat food insecurity.
The BBC WST and partners Internews are collaborating through the “infoasaid” project to help ActionAid provide timely information to pastoralists, to help combat food insecurity.
Weekly information about livestock and food commodity prices in Isiolo market – the main reference market for the region – is sent through SMS messages (using FrontlineSMS software) to field workers in rural communities, who post the information on local noticeboards.
Given high illiteracy rates in the area, the project is also providing a recorded message service using Freedom Fone that allows people to listen to local Swahili updates.
The bulletins help drought-distressed pastoralists to keep tabs on the price of staple foods such as maize, beans and vegetable oil on which they increasingly depend.The bulletins help drought-distressed pastoralists to keep tabs on the price of staple foods such as maize, beans and vegetable oil on which they increasingly depend. The market information also allows them to achieve better prices for the animals they sell to traders – boosting cash household income.
Local news and information given alongside market prices also contain useful tips on issues affecting the well-being of animals. Items will include updates on rainfall, outbreaks of animal disease and de-stocking programmes.
Together, the two channels allow pastoralists living in isolated communities to access reliable and up to date market information. They also allow ActionAid to keep in closer touch with the village relief committees that handle food distribution to individual families.
250 basic mobile phones and solar chargers purchased as part of the project are also being used by village relief committee members who live in or near locations with network coverage.
The cheap and durable solar chargers are vital in areas without electricity. They can also provide a source of revenue (as they charge other mobile phones for a modest fee) that allow relief committees to purchase vital air time for their phones.
Faster data
An additional aim of the Isiolo project is to speed up ActionAid’s collection of data from the field.An additional aim of the Isiolo project is to speed up ActionAid’s collection of data from the field.
FrontlineSMS allows ActionAid to transmit electronic forms to field staff in Isiolo County via mobile phone. These are filled in electronically and dispatched immediately to the regional office through SMS messages.
These FrontlineForms are now being used to transmit time-sensitive reports on issues such as food distribution, food for work activity, malnutrition rates and local food prices. The information arrives rapidly in a standard format which is easy to analyse.
In the long term, this will help ActionAid to ensure its humanitarian aid activities in Isiolo are more effective and more responsive to the needs of the local population.
Communication as aid
In any emergency, be it natural disaster or man-made, long- or short-term, people's lives are turned upside down. Knowing what's happening, where to go for assistance and who to call for help is crucial to their survival and recovery.
The goal of the 'infoasaid' project is to help humanitarian organisations integrate two way communications with affected communities into their emergency programmes. This in turn improves the effectiveness of aid delivery.
As the drought and famine crisis in the Horn of Africa deepens, such communication is more important than ever.
A new 'Communication is Aid' animation, produced by infoasaid, demonstrates the positive impact of two way communication with crisis affected populations.
Read more about the work of infoasaid on their website.
Texting for life in Pakistan: the International Organisation of Migration
The International Organisation for Migration, an intergovernmental organisation working to support people to return to their homes after being displaced by disaster of conflict, have been using FrontlineSMS in Pakistan for some months. Below, the twenty-eighth FrontlineSMS guest post is an operational update from Maria Ahmed and Isabel Leigh, in the Mass Communication Team.

October 15th is Global Handwashing Day, and in Pakistan, the IOM have been sending messages about hygiene and sanitation as part of their response to the devastating floods that hit Pakistan in recent months, affecting approximately 20 million people according to the UN's Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Aid (OCHA).
IOM are leading the communication response on behalf of the UN 'Cluster System' of humanitarian responders, and have developed over 50 Public Service Announcements (PSAs) in Pashto, Sindhi and Punjabi on topics including prevention of diarrohea and malaria, water purification methods, mother and child health during the fasting month of Ramadan, child protection issues, treating snake bites, setting up durable shelters and fire safety in camps.
IOM first started using FrontlineSMS in the North in 2009, to mirror humanitarian messages sent out using radio broadcasts with informational texts. People in Northern Pakistan, nearly 3 million of whom were displaced by conflict in 2009, use cell phones extensively amongst family members, often texting in Urdu ( the national language) using the English script. Using FrontlineSMS has saved IOM over $15,000 compared to the costs they would have paid to develop an organised, mass texting system using a commercial supplier. Supported by Zong, the Pakistani subsidiary of China Mobile, IOM is sending free, bulk, informational messages to affectees and humanitarian workers across Pakistan to enhance informational outreach.
In the South, people are used to using mobiles for voice calls, but send far fewer text messages. So IOM are partnering with Zong, who have donated a million free phone calls through 100 cell phones to IOM to enable a free phone service for flood victims to get vital information, seek help and access relief services offered by the Government and aid agencies. IOM hope to continue to expand the service to reach more handsets in Sindh, Punjab and KP, and from January onwards, in Balochistan, Gilgit Baltistan and Pakistan Administered Kashmir.
TSF, FrontlineSMS and humanitarian assistance in Niger
In this - the third in our series of FrontlineSMS guest posts - Grégory Rebattu, Télécoms Sans Frontières (TSF)’s Niger Representative, and Oisín Walton, Head of TSF Communications and International Relations, talk us through their thoughts on the software, and its potential for emergency relief in Niger. "I work for Télécoms Sans Frontières (TSF), the leading NGO specialising in the deployment of telecommunications in emergencies, and head-up TSF’s base here in Niger. In emergencies, telecommunication networks are often seriously damaged or destroyed. Some humanitarian crises also strike in areas with no existing communication facilities. Today, TSF plays a key role in strengthening coordination and communication by deploying telecommunications centres within 48 hours of an emergency. These centres offer broadband Internet access, voice communications, fax lines and all the IT equipment needed for a field office.

Our base in Niger is more involved in longer term projects particularly in strengthening food crisis prevention systems. Niger is ranked 174th out of 177 nations on the United Nations Development Programme’s Human Development list - making it one of the least developed countries on Earth. The living conditions in the Sahel desert are extremely harsh and recurrent drought leads to almost permanent food insecurity. Less than 12% of the territory is cultivable - so the widely reported current food crisis hits Niger particularly hard.
Telecommunication networks are also very much in their infancy, although GSM coverage is now on the rise and bringing infinite new opportunities for the humanitarian and development sectors. In particular, we believe that text messaging – used in conjunction with cutting-edge tools such as FrontlineSMS - are particularly powerful, enabling the collection and dissemination of data quickly and easily with very low running costs. Over the past few weeks we have been working closely with the FrontlineSMS team, putting the software through its paces and assessing its suitability in our work. We have been particularly excited by the new “FrontlineSMS Forms” data collection functionality which we helped test and which is being released next week.
Crucially from our perspective, FrontlineSMS is extremely user-friendly, allowing partner organisations on the ground to rapidly deploy a data collection and dissemination system from scratch. This simplicity is crucial for organizations which may lack technical skills, and users can be up and running in a matter of minutes with the minimum of mouse clicks. The intuitive nature of the software also means that little technical support is required once they’re up and running.
I have already presented the application to a group of NGOs and UN agencies who are very excited. These organizations - who work in a wide range of sectors including health, nutrition and agriculture - immediately saw the immense potential of FrontlineSMS and how it might enhance their capacity to save lives and develop local economy, not to mention their capacity to improve the security of their own staff.
On that note, our first FrontlineSMS initiative is about to launch, and will provide an SMS security alert forwarding service to Niger’s NGO community. This will allow aid workers to instantly warn the community about security issues in real time.

Concretely, we see other immediate applications for FrontlineSMS in Niger. These include the use of the new Forms feature for data collection for the National Health System which collects and monitors the number of cases per pathology in health structures. FrontlineSMS could also be used to collect market prices, and even to disseminate those prices to small farmers.
We are also planning to test its interoperability with satellite phones which will allow us and our partner organizations to extend its usage into areas not covered by mobile networks. We also plan to use it in our responses to sudden-onset emergencies where mobile networks are often disrupted.
Summing up, FrontlineSMS is a fabulous tool and one which presents huge opportunities to non-technical NGO users. Saying that, don’t be fooled by its simplicity – as well as standard incoming and outgoing group messaging, it has plenty of advanced and extremely powerful functionality. From our testing and evaluation, and our discussions with partner organizations, it looks like FrontlineSMS has infinite applications in the humanitarian world, and this is great news for those we are trying to help.
As we often say here, it’s now no longer a question of technology, it’s a question of imagination!"
Grégory Rebattu, Niger Representative Oisín Walton, Head of Communications & International Relations Télécoms Sans Frontières www.tsfi.org