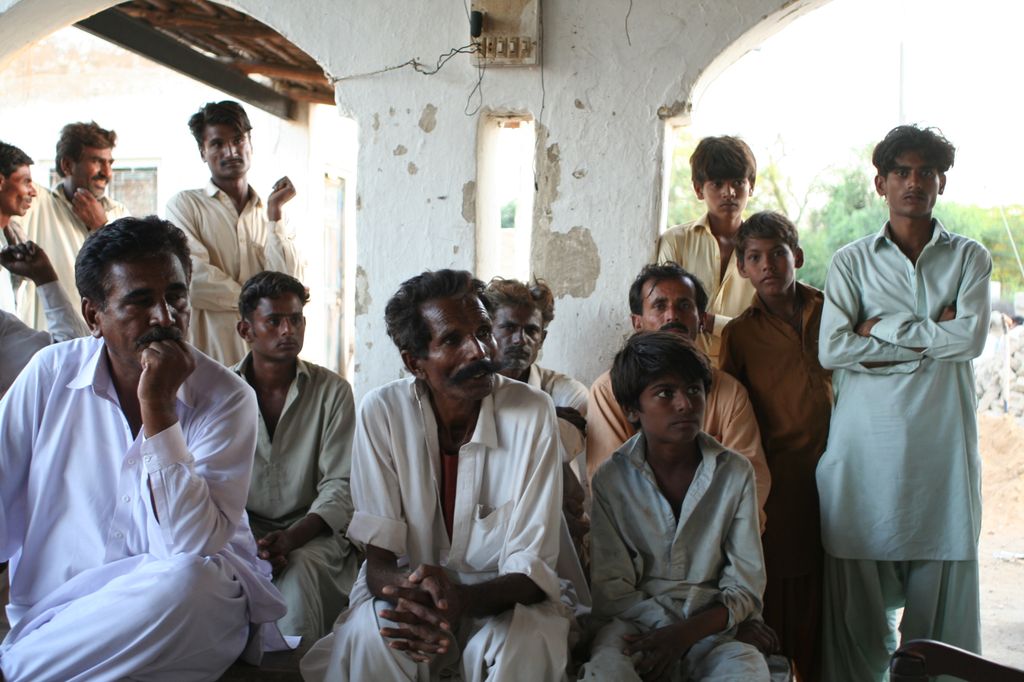
In this guest post, Alex Gilchrist explains how the Popular Engagement Policy Lab (PEPL) used SMS to communicate with affected communities during the humanitarian response to the floods in Pakistan in 2011. Using FrontlineSMS to set up a Complaints and Response Mechanism, people were able to share their experiences of accessing food and shelter. Co-authored by Syed Azhar Shah from Raabta Consultants, this post demonstrates how it is through the effective use of communications technology that people can be connected to the services they need the most. Guest Post by Alex Gilchrist, Popular Engagement Policy Lab and Syed Azhar Shah, Raabta Consultants
The 2011 monsoon flooding in Sindh, Pakistan’s southernmost province, affected an estimated 5.5 million people. The floods compounded the damage caused by flooding in 2010 and the lack of clean drinking water, food, healthcare and shelter resulted in communicable and non-communicable diseases across the province. It also caused loss of livelihoods through damage to agricultural land and death of livestock that will continue to affect the lives of the people of Sindh for years to come.
In the aftermath of the recent flooding, a large Pakistani NGO called Strengthening Participatory Organisation (SPO), which manages a network of organizations across Sindh province started a new project in Mirpur Khas district, distributing food items and shelter to those worse affected. Following an assessment process for one of its smaller projects, SPO selected a total of 475 beneficiaries across 24 villages.
A concern of SPO’s head office in Islamabad was that complaints and feedback from beneficiaries in previous projects had not been documented or dealt with effectively and they wanted to monitor the distribution process. This is when the Popular Engagement Policy Lab (PEPL) and Raabta Consultants were asked to help.
We were asked to set up a mechanism through which people could register issues they encountered during the flood relief distribution project in order to improve accountability and transparency before, during and after the distribution had taken place. PEPL develop research methodologies, specializing in innovative uses of low- and high-tech information systems, and for this project we collaborated with Raabta Consultants, who help communities in Pakistan to access the valuable social services provided by governments, NGOs, charities and the private sector. Using FrontlineSMS, we developed a system to handle SMS-based feedback from affected communities as part of their new Complaints and Response Mechanism (CRM).
Although less than half of Pakistan’s population owns a mobile handset, recent research indicates that more than 70 percent of people have regular access to a mobile phone. Amongst phone owners in the poorest 60 percent of Pakistan’s population, 51 percent of men and 33 percent of women used SMS, according to a survey by LIRNEasi in 2009. We wanted to test whether we could harness the prevalence of mobiles and the use of SMS for improved accountability.
Beneficiaries of the project were selected in virtue of being the most disadvantaged in each village: often those with disabilities; child-headed households; or female-headed households, and literacy rates among them were low. We realized it would be a challenge to design a system that would be accessible and useful across the board. To put these concerns to the test, we conducted a questionnaire involving participants of both genders on mobile phone usage. To the surprise of the project team the overwhelming response was that access to mobile phones was widespread, and if someone did not own a mobile phone then they could borrow one from a family member, friend or even village council member and even ask someone to write a message on their behalf. Through this evidence about the culture of using mobile, we gained overwhelming support for a system to base the CRM on a combination of text messages and voice calls.
The next step was to configure a system using FrontlineSMS so that people could text us requesting a call back. Sindhi is largely written in Arabic text, but not all handsets can recognize the Unicode in which it appears. So, following the conversations with villagers, the team devised a numbering system for complaints ranging from 1-0. The code was as follows: 1 = Food items, 2 = Shelter, 3 = Conflict 4 = Corruption, 5 = Issues with SPO staff, 6 = Issues with Partner Organisation staff, 7 = Issues with Village Council, 8 = Issues affecting women and children, 9 = Issues affecting those with disabilities, and 0 as a means of saying “thank you”. This numbering system allowed for automatic replies through FrontlineSMS tailored to the complaint, as well as a response time.
The numbering system was printed on cards with corresponding pictures, and the SMS and feedback system was also explained through diagrams. On the cards we included telephone numbers for verbal complaints and instructions for written complaints. Having printed out leaflets, posters and cards the teams went to every village and explained the process to beneficiaries and non-beneficiaries alike. During this process, field workers documented all beneficiary phone numbers or relatives’ and friends’ phone numbers, which were then saved in FrontlineSMS. This meant that every message received in FrontlineSMS would also have a name attached to it, and the system was set up so that every auto reply contained the name of the sender. We believe that the in-person relationship is a critical step that makes the difference in the popular uptake of a communications system.
Through the groups feature on FrontlineSMS, we created lists for village and Union Council members so that before each aid distribution process SPO could send messages alerting the beneficiaries about its arrival, and following the distribution process we could actively solicit feedback via SMS. When a message was received, the response manager would call back, ask for more information and then follow the internal complaints procedure.
Over the three-month aid distribution project we received 725 messages, 456 of which followed the numbering system. The awareness of this system amongst partner organizations and project staff meant that they knew they were being held to account for their actions, so it ensured the quality of their work. It was especially important that the system protected the identity and data of participants in a way that could not be tampered with. Fundamentally, we learnt that giving people a direct means with which to register a complaint or feedback empowered the beneficiaries of the relief effort to have a say in the way they were treated and furthermore to be connected with organizations who could offer further support.