Over the last decade, we’ve changed leadership, structure, and product – but what hasn’t changed is our values. Here are 5 of our favorites:
Frontline Honored by Nominet 100 2014
Frontline at Nine
Homes for the holidays
Landesa and FrontlineSMS are delighted to welcome and share the announcement today of a US $1.5m Google Global Impact Award, which will enable them to use mobile technology to transform the way that the government in the Indian state of Odisha helps landless families gain secure rights to their land and homes.
Kicking conflict into touch with FrontlineSMS - a post from National Geographic
Njenga Kahiro, Kinship Conservation Fellow and member of the Zeitz Foundation, started the Laikipia Unity Cup in 2010 when he decided to combine environmental education and a football tournament. Laikipia is a countyin central Kenya where conflict between warring communities and stripping of natural resources are both fairly common. Njenga, with the help of his foundation, put together football teams from each region , usually combining young citizens of quarreling communities, and host a tournament that included matches, educational theater, and local conservation projects.
FrontlineSMS Named #1 Tech NGO in the World by the Global Journal
On the same day that the Global Journal announced us as their pick for “#1 Tech NGO in the world”, my laptop died. As my coworkers celebrated our newly-bestowed honor, I relished the irony of my technological failure and felt what has come to define my time working in the non-profit world: humility.
Low tech adaptations for a community communications system
For the past month, I’ve been in Sudan working to set up the information flows and tech that will support SUDIA’s Community Communications System. From the tech and information management perspective, SUDIA’s System is interesting because it adapts to a low tech environment by integrating SMS and radio, and processing information largely offline. The System collects and disseminates information useful to communities that live along the migratory routes in Blue Nile State. It focuses on information that communities themselves can use to make their livelihoods more sustainable and more peaceful. In other words, the System is not aimed at organizations (Government or non-Government) that can use information to provide services or design interventions. Rather, it is aimed at communities helping themselves, and provides information that is useful to community leaders in organizing local community responses to livelihood challenges.
FrontlineSMS case study featured in new Rockefeller Foundation report: Learning from experimentation
The Rockefeller Foundation recently launched a new website, Capacity to Innovate.org, which examines lessons from a number of organizations including Ushahidi and Internews, and encapsulates them in three short reports which are well worth a read. FrontlineSMS is featured in the 'Learning From Experimentation' report, available from the website. Here's an excerpt, but we really recommend the whole report as a very readable and thought-provoking set of examples.
Guardian: Africa's apps: Farming to Gaming
In Kenya, microfinance is going mobile - Part 2
The FrontlineSMS:Credit team was recently interviewed by Claire Penicaud at the GSMA MMU about the challenges that Micro Financing Institutions (MFI) face when thinking about adopting mobile money. The FrontlineSMS:Credit team described the challenges they see MFIs in Kenya facing and gave the following pieces of advice to MFIs who are ready to integrate mobile money into their systems.
FrontlineSMS
FrontlineSMS:Credit enables organizations that serve the base of the economic pyramid to bring the benefits of mobile money to the financially excluded by building and distributing free, open-source software for mobile money management.
FrontlineSMS:Credit’s PaymentView software is an extension of FrontlineSMS’s free, open-source technology that turns a laptop and a mobile phone or GSM modem into a central SMS communications hub. The tool enables users to send and receive text messages with large groups of people without the need for Internet access. With thePaymentView extension, users can also send, receive, and manage mobile money transactions. By expanding the uses of mobile money in developing markets, FrontlineSMS:Credit helps to fulfill the promise of mobile money to offer even the most underserved communities access to financial services and enable new business models that aid in development.
A lot has happened since we last talked to the FrontlineSMS: Credit team. In a previous blog post, we described their approach towards enabling organizations and businesses to easily use mobile money. Over the past few months, they’ve got the opportunity to test this approach through a project in partnership with a Kenyan financial services association (FSA) [1].
Challenge #1: Providing an easy and convenient way for groups to transfer money to the FSA…
This FSA is composed of 50 groups of around 20 people each. Like many others, it serves a large geographical area and some groups are more than 30km away from the FSA head office. This means that a representative of each group has to travel there every time the group wants to transfer money: which represents a day of travel for the representative of the group and a cost of around USD8 for the group on a monthly basis. The service implemented by FrontlineSMS: Credit allows representatives of groups to transfer money through M-Pesa directly to the FSA. FrontlineSMS estimates that there has been a reduction of up to 50% in the cost of repaying loans and a reduction of up to 85% in the time spent on repayments, depending on how far away a savings group meets from the FSA office. The groups saving the most are those who are far away from the FSA, as almost every group meets within a short walking distance of an M-Pesa agent.
Read the full post on the GSMA website.
How technology democratised development
On September 7th 2012, our founder Ken Banks contributed a guest article to BBC Future, their website on technology, science, the environment and health, on the impact technology has on poverty eradication.
"Twenty years ago, if you were information technology-literate and interested in international development, your options were limited.
That’s how things were for me when, in 1993, armed with ten years programming and networking experience I began turning my attention to the developing world.
My efforts didn’t get me far. The information technology revolution we see today had barely started at home, let alone in many of the developing nations. If you weren’t an English teacher, a doctor, a policy maker, an economist or a dam builder, careers in development seemed somewhat limited.
How things have changed. Driven largely by the spread of the world wide web and the burgeoning mobile phone sector, opportunities to develop solutions to many of the world’s social and environmental problems have reached almost every bedroom and garden shed in the land.
The irony today is that arguably the greatest developmental tool we have in our hands isn’t a product of the tens of billons of developmental aid spent over the years, but a by-product of private sector investment. Putting the debate around costs and coverage to one side, the development sector has a lot to thank the mobile industry for.
In 1993 the number of mobile subscribers in Africa numbered in the hundreds of thousands. By 1998 that had crept to four million. Today there are an estimated 735 million with penetration running at around the 70% mark. Not bad in less than 20 years."
You can read more on the BBC Future website. UK readers can access the article on Ken's website.
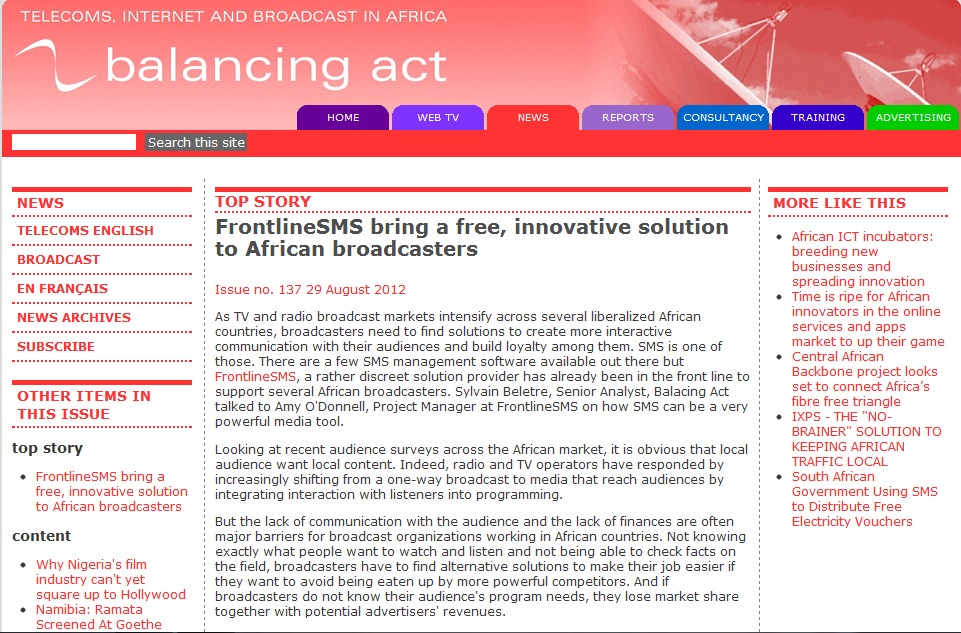
FrontlineSMS bring a free, innovative solution to African broadcasters
As TV and radio broadcast markets intensify across several liberalized African countries, broadcasters need to find solutions to create more interactive communication with their audiences and build loyalty among them. SMS is one of those. There are a few SMS management software available out there butFrontlineSMS, a rather discreet solution provider has already been in the front line to support several African broadcasters. Sylvain Beletre, Senior Analyst, Balacing Act talked to Amy O'Donnell, Project Manager at FrontlineSMS on how SMS can be a very powerful media tool.
Looking at recent audience surveys across the African market, it is obvious that local audience want local content. Indeed, radio and TV operators have responded by increasingly shifting from a one-way broadcast to media that reach audiences by integrating interaction with listeners into programming.
But the lack of communication with the audience and the lack of finances are often major barriers for broadcast organizations working in African countries. Not knowing exactly what people want to watch and listen and not being able to check facts on the field, broadcasters have to find alternative solutions to make their job easier if they want to avoid being eaten up by more powerful competitors. And if broadcasters do not know their audience's program needs, they lose market share together with potential advertisers' revenues.
To read more, please click here.
The Unheard Millions: A New Audience Joins Global News Conversations
On Friday, August 31st 2012 PBS featured a blog post written by Trevor Knoblich, our Media Project Manager. The post focused on our plans to integrate journalism tools into FrontlineSMS, enabling news-gatherers all over the world to integrate SMS more easily into their work. Thanks to PBS for allowing us to repost the piece here - you can find the original on the PBS Media Shift website. If you are interested in hearing more about our work, please email services@frontlineSMS.com to get in touch with the team.
By Trevor Knoblich, Media Project Manager
The field of journalism has faced a number of technology-driven changes in the past decade, including the advent of blogs, the generating and sharing of news via social media, and the tentative move by many governments to provide open data.
So many elements of news have evolved that many experts think we're on the verge of a revolution in digital journalism, including Google's director of news and social products, Richard Gingras. "The media landscape is in the process of being completely transformed, tossed upside down; reinvented and restructured in ways we know, and in ways we do not yet know," Gingras argued recently during a keynote address at the annual conference of the Association for Education in Journalism and Mass and Communication. "The process of change is far from over. Indeed, it will never be over."
NEWS AS A PARTICIPATORY PROCESS
When thinking about all of these changes, I find one shift particularly inspiring: the growing concept of news as a participatory process. In the past, news was produced largely by media outlets and consumed by readers, viewers, or listeners -- a passive audience. Of course, now we view news as a lively and active discussion, in which former "consumers" participate in sharing stories, providing news tips, raising questions, and adding depth and context to stories.
Chris Lehmann, former chief of Yahoo News, recently told the New York Times' David Carr, "News is an activity, a verb really." He was primarily referring to the editorial room, but I think this now equally applies to all people who regularly read, share, write, and contribute to news. We live in an active news culture, in which stories are rarely static, breaking news reaches the world in a matter of seconds, and average citizens have access to many tools to provide news tips, content, and context nearly instantaneously.
This access has been described as public, participatory or citizen journalism, with varying definitions for each -- and no definition that everyone can agree on. That said, regardless of the title we give to this shift in news culture, the combination of ways in which people can contribute to news is encouraging. The more people are seeking, discussing, and shaping information, the closer we may get to a common understanding of the issues and challenges we face in our community, region, nation, or planet. This shift also allows information to spread quickly, and reach more people.
EXPANDING GLOBAL PARTICIPATION
With this in mind, I accepted my role at FrontlineSMS with a specific purpose: to extend global participation in news to people who otherwise would be left out of this shift, meaning those with no or infrequent access to the Internet. Lack of Internet access should not exclude people from receiving, discussing, and shaping the news that affects their lives. And while many people still lack Internet access, nearly everyone has access to a mobile phone, and by extension SMS.
SMS is the most pervasive digital communications platform in existence. As such, news outlets can use SMS to invite more people to participate in news in a variety of ways. Participants may be trained citizen journalists, eyewitnesses sharing news tips or photos, or even commentators on important stories.
Yes, this brings with it the challenge of vetting information, verifying senders, and devising clever mechanisms for being inclusive of a variety of different voices. But I believe we can meet those challenges, and the result will be a more robust audience participating in news in a more informed way. In fact, I've already seen inspiring examples of this from our user base at FrontlineSMS.
In one example, Al Jazeera noticed that while many people around the world were discussing the viral, controversial Kony 2012 video, there was a glaring gap in input from people in Uganda, where much of the discussion is focused. In response, Al Jazeera established the Uganda Speaks program, allowing people in Uganda to join the conversation in a variety of formats, including SMS, e-mail, Twitter and Facebook. For those without Internet access, SMS became a critical channel to weigh in on the global dialogue.
In another example, Indonesian television station RuaiTV trained citizen journalists in a method for texting information on illicit activities by palm oil companies. Citizen journalists would text or call with information about suspected wrongdoings, and RuaiTV would follow up on the news tips. In this manner, citizens were actively working to hold companies and governments accountable to the local legal framework.
At FrontlineSMS, we are motivated by these and similar user stories. These organizations are working to lower the barriers for participating in news debates, whether they are local or global. Via SMS, we can now invite many more people to receive news, share new ideas, and foster discussion around topics that are important to them. In many cases, people have this type of access for the first time in their lives. Thanks to the creativity of our users, potentially millions of new voices are now invited to participate in news. It will be thrilling to hear what they have to say.
Trevor Knoblich works as Project Manager for FrontlineSMS, a 2011 Knight News Challenge winner. He began his career as a federal policy reporter in Washington, DC,then spent 5 years working as a humanitarian specialist. He currently works on issues at the intersection of journalism, technology and developing countries. At FrontlineSMS, he is building tools to help journalists and media outlets around the world improve their ability to gather, track and share news.
Interview with European Journalism Centre Magazine: Is FrontlineSMS:Radio Advancing Social Change in Africa?
Amy O’Donnell, Radio Project Manager at FrontlineSMS:Radio recently spoke to Alessandra Bajec from the European Journalism Centre Magazine about the way FrontlineSMS is used to facilitate dynamic conversations between radio stations and their listeners in Africa and beyond. By enabling the powerful combination of radio broadcasting with SMS, FrontlineSMS:Radio is empowering and engaging communities across the globe. Republished here with permission or you can read the original post here. By Alessandra Bajec
Q. How has FrontlineSMS technology influenced African media?
Exponential growth in use of mobile technology has meant that many African media outlets are interested in using this technology effectively. By downloading FrontlineSMS and plugging in a mobile phone or GSM modem to a computer, people can use SMS in more sophisticated and professional ways.
We are moving from having contributions fed via SMS into an individual’s phone to a more open way of integrating SMS into content. We’re also supporting citizen journalists with tools for digital news gathering.
In Zambia, for example, Breeze FM radio uses FrontlineSMS to communicate with journalists. After gathering news tips received from the general public, the radio station organizes the evidence, sends SMS to journalists who may be out in the field, encouraging them to verify the facts and report.
Q. What is innovative about the FrontlineSMS software plugin?
With Version 2 recently released, FrontlineSMS has a user-friendly interface making it easier to manage larger volumes of messages, and to customize the software to better meet user needs. Pending messages can be sorted in a more timely fashion.
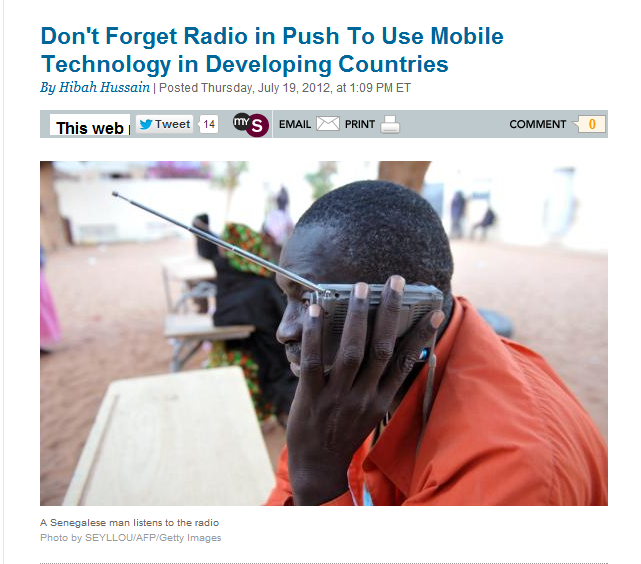
Slate.com features FrontlineSMS usage for a Radio station in Malawi
So radio is important—but not perfect. Although community radio stations often involve local residents in programming and long-term planning, getting real-time feedback from listeners can be challenging. Voice calls are expensive, and stations have a limited time to take calls from their audiences. This is where mobile telephony and text messaging can be a game changer, transforming radio listeners into active participants.Another example: FrontlineSMS, an organization devoted to leveraging mobile phones for development. Unlike similar organizations, Frontline has devoted significant resources to radio initiatives. Frontline’s platform has been used by community radio stations like Radio Mudzi Wathu in Malawi, which uses Frontline SMS to solicit questions, comments, and ideas from listeners. During prime listening hours, Radio Mudzi asks its audience questions like “why do you think that HIV/AIDS is increasing despite interventions?” and asks them to text their responses. They then aggregate the responses, analyze them, and take them to local policymakers and aid workers.
In addition to facilitating audience participation, SMS-oriented radio initiatives allow for unprecedented levels of audience research. After receiving feedback on any given issue, stations have a repository of information that they can analyze and look back on in order to better serve needs of audience. As they identify trends, needs, and concerns, radio stations can catalyze a profoundly fruitful cycle, using more relevant programming to drive audience engagement, thereby soliciting more feedback and dialogue.So how can we encourage more hybrid radio/mobile projects? First of all, we need to adjust the way we approach technology intended for the developing world. When designing, funding, researching, or discussing technology for development projects, we need to stop being fixated on one technology or platform and instead consider how new technology can be integrated with existing needs, values, and networks.